FIG. 1.
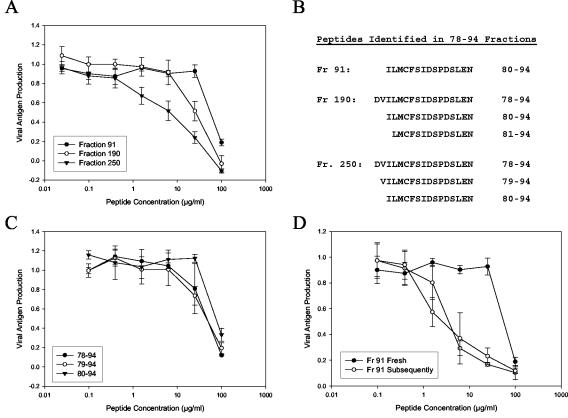
The antiviral activity of a RhoA-derived peptide preparation is highest in late-eluting aggregates and aged peptide aliquots. A crude peptide corresponding to the sequence from residues 78 to 94 of RhoA was synthesized and subjected to fractionation by reverse-phase HPLC. A total of 300 fractions were collected, and selected fractions were tested for antiviral activity. (A) Inhibition curves for the three fractions with the highest activities. (B) The fractions shown in panel A were analyzed by mass spectrometry to identify peptide products. Shown are the peptide sequences that likely correspond to the observed masses. For fraction 250, the validity of these assignments was verified by sequencing. (C) The peptides identified as components of fraction 250 were individually synthesized and tested for antiviral activity. (D) Compiled data from multiple assays of peptide 80-94 from fraction (Fr) 91. Closed circles, the first test of a peptide aliquot after it was dissolved; open circles, subsequent tests of the same aliquot. Results are representative of several tests with both crude and purified 80-94 peptides. Each datum point represents the mean for three replicate wells at each concentration, and error bars represent the standard deviations.
