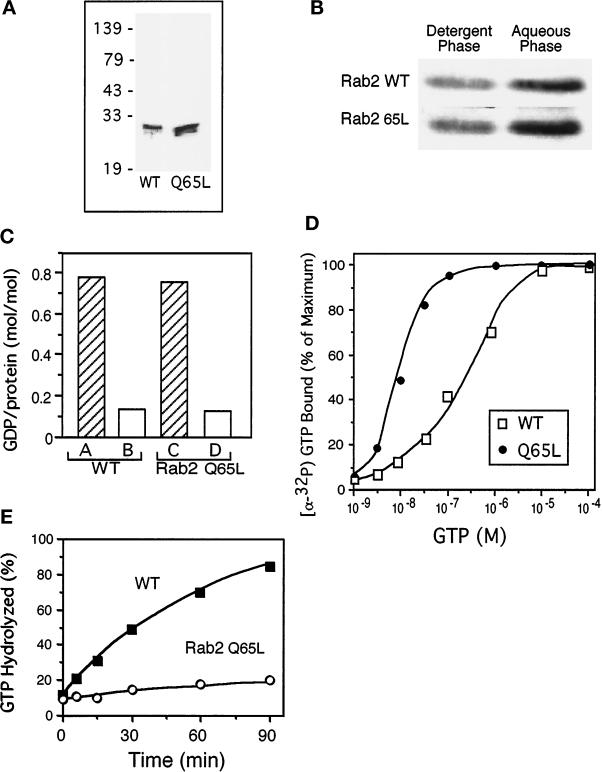
Figure 1.
Guanine nucleotide–binding properties of bacterially produced Rab2 proteins. (A) Rab2 wild type and Rab2 Q65L were purified after expression in E. coli using ion exchange chromatography and gel filtration. The proteins were analyzed by separation on SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining, and then the gel was scanned on a densitometer. The recombinant proteins were found to be ∼90% pure. (B) The purified proteins (0.5 μg) were prenylated in an in vitro reaction and then subjected to phase partitioning in Triton X-114, and the distribution of the Rab2 proteins was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. The prenylation efficiency is ∼40–45% as indicated by partitioning with the detergent-rich phase. (C) Rab2 and Rab2 Q65L (10 pmol) were incubated for 1 h with 2.5 μM [3H]GDP (∼500 cpm/pmol) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA and 4.5 mM MgCl2 (bars A and C) or 10 mM MgCl2 (bars B and D), and the amount of protein-bound [3H]GDP was determined as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. The recombinant proteins are ∼70–75% active based on their ability to bind and exchange GDP. (D) Equilibrium binding of [α-32P]GTP by Rab2 wild type and mutant is shown. Rab2 proteins (10 pmol) were incubated for 60 min at 30°C with increasing concentrations of [α-32P]GTP (1 × 10−9 to 1 × 10−4 M). Protein-bound [α-32P]GTP was captured on nitrocellulose membranes and then quantitated by liquid scintillation counting as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. The results are normalized to the amount of binding at the highest concentration of [α-32P]GTP for each protein. (E) GTPase hydrolytic activity was measured by in-cubating Rab2 and Rab2 Q65L with [α-32P]GTP at 37°C. At the times indicated, the reactions were terminated with the addition of ice-cold 0.5 M EDTA, and the [32P]-labeled nucleotides bound to the proteins were analyzed by TLC. Results shown in all panels are representative of three independent protein purifications.