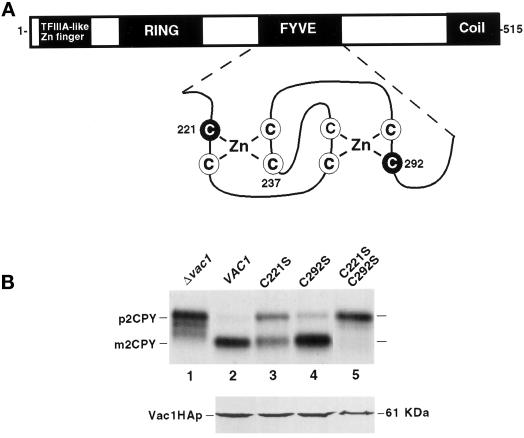
Figure 5.
Characterization of vac1 FYVE finger mutations. (A) Vac1p consists of the following previously identified domains: a C2H2 TFIIIA-like zinc finger located proximal to the N terminus, an H6 variant zinc-binding RING finger, a zinc-binding FYVE RING finger, and a region predicted to form coiled coil structures located at the C terminus (Burd et al., 1997). Shown below the FYVE finger is an enlargement of the predicted structure of this domain along with the highlighted cysteine residues that have been mutated to serines individually or in combination (C221S, C237S, and C292S). (B) The abilities of yeast strains expressing vac1 alleles encoding Vac1 proteins with mutant FYVE domains to sort CPY were assessed. GTY104 (SEY6210; vac1Δ3:: NEO; lane 1) was transformed with plasmids pGT1-1 (WT VAC1) (lane 2), pGT1-4 (C221S-vac1) (lane 3), pGT1-6 (C292S-vac1) (lane 4), and pGT1-7 (C221/292S-vac1) (lane 5). CPY was immunoprecipitated from the labeled lysates that were generated from these strains as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS and in Figure 4 but at 30°C (upper panel). The expression levels of C-terminal HA-tagged Vac1p FYVE finger point mutants were also examined under steady-state conditions. GTY104 (1.0 OD600 equivalent) expressing the following HA-tagged vac1 alleles were lysed in urea sample buffer: pGT1-17 (WT Vac1HA) (lane 2), pGT1-18 (C221S-Vac1HA) (lane 3), pGT1-19 (C292S-Vac1HA) (lane 4), and pGT1-20 (C221SC292S-Vac1HA) (lane 5). The lysates were resolved by SDS-PAGE, and the Vac1HA proteins were identified by Western blot analysis using HA antibodies. Vac1HAp was detected using the Blaze chemilluminescent detection system (lower panel).