Figure 5.
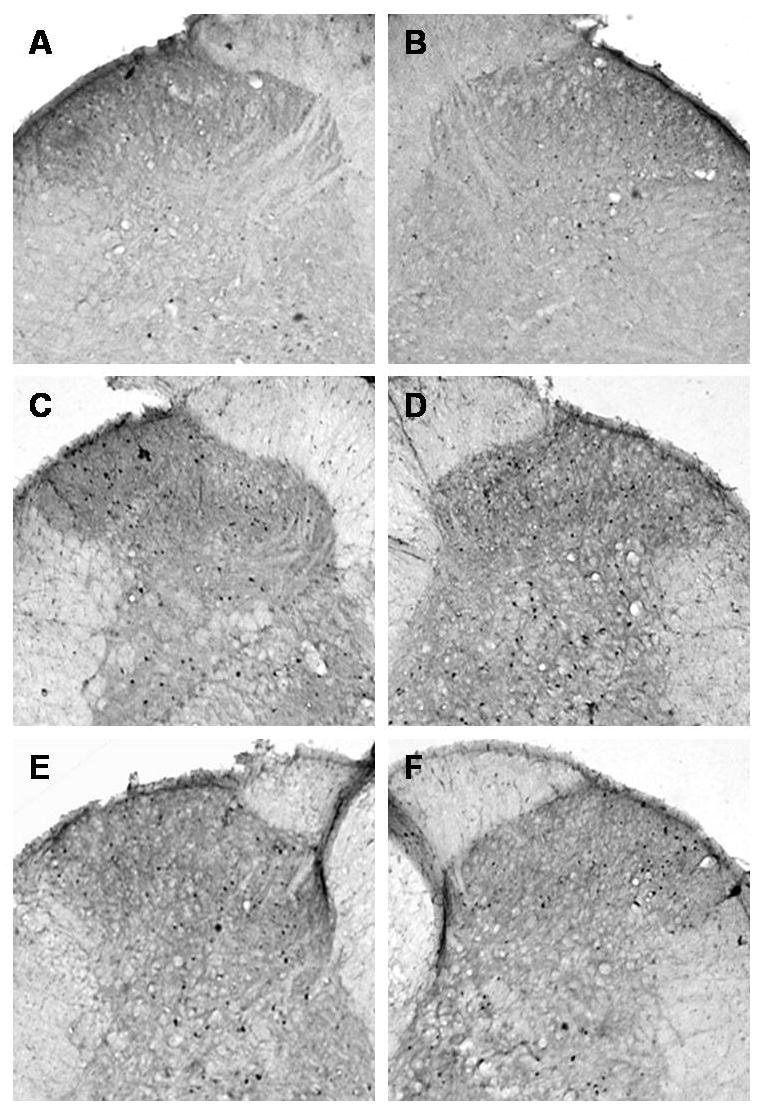
Microphotographs illustrate the distribution of Fos-IR neurons in the lumbar (L4-L5 segments) spinal cord dorsal horn. All images of the spinal cord were captured with a 4X objective. Panels A and B demonstrate the right and left sides, respectively, of a control rat spinal cord section. Panels C and D demonstrate the ipsilateral and contralateral sides, respectively, of a tibia fracture rat treated with vehicle. A dense Fos immunostaining can be seen in the superficial laminae (I and II) and through the deep laminae in the ipsilateral (C) and in the contralateral dorsal horn (D). Treatment with anti-NGF antibodies partially blocked the fracture-induced increase in Fos-IR in the ipsi- and contralateral dorsal horn (E and F respectively).
