Table 1. Distribution characteristics for the measured and estimated deviations.
| Subset size, k | Median deviation | Trimmed mean | Median absolute deviation | Interquartile range | AUC value |
| Measured | −0.0141 | −0.0152 | 0.0267 | 0.0169 | 0.662 |
| 28 (Initial set) | 0.0000217 | 0.00107 | 0.0209 | 0.0147 | 0.772 |
| 136 | 0.000687 | 0.000388 | 0.0202 | 0.00958 | 0.810 |
| 208 | 0.00134 | 0.00118 | 0.0141 | 0.0108 | 0.773 |
| 317 | −0.000634 | −0.000816 | 0.0173 | 0.0120 | 0.679 |
| 323 (All pairs) | −0.000634 | 0.00142 | 0.0236 | 0.0169 | 0.730 |
The rows correspond to distributions of the estimated deviations 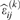 with different sizes of subsets of those gene pairs used in the approximation process (see Figure 4). The distribution of the measured deviations εij is used as a references value for the different parameters (the first row). As robust measures of location (bias) and dispersion (variability), we calculated the trimmed mean and interquartile range, respectively, in addition to the median and median absolute deviation that were used in the previous comparative study [14]. The bold type indicates the subset size which provided the most accurate prediction of the functional links in terms of the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC).
with different sizes of subsets of those gene pairs used in the approximation process (see Figure 4). The distribution of the measured deviations εij is used as a references value for the different parameters (the first row). As robust measures of location (bias) and dispersion (variability), we calculated the trimmed mean and interquartile range, respectively, in addition to the median and median absolute deviation that were used in the previous comparative study [14]. The bold type indicates the subset size which provided the most accurate prediction of the functional links in terms of the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC).
