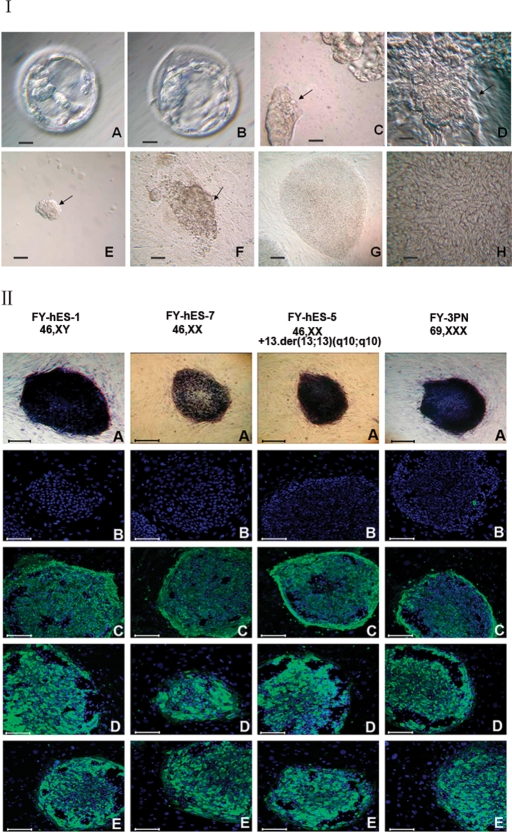
Figure 1:
Derivation of hESC lines and characteristics.
(I) Human embryos and isolated ICM. (A) A Day 5 blastocyst cultured in G2.3 blastocyst medium. Note the small ICM. (B) A Day 7 blastocyst that has been cultured in the blastocyst optimum medium for another 2 days. The ICM became clearer. (C) An ICM isolated by mechanical method. (D) A round ICM colony surrounded by a group of residual trophectoderm after mechanical isolation. (E) An ICM isolated by immunosurgery. (F) A dome-like structure on the feeder layer formed after 8 days culture of ICM isolated with immunosurgery. Arrows in C to F indicate ICMs. (G) Typical round hESC colonies with very clear boundary at low magnification. (H) hESC morphology in a colony, showing a high nucleus–cytoplasm ratio; note the presence of nucleoli and typical intercellular spaces at high magnification. Bar = 25 µm in A, B, C and D and bar = 100 µm in E, F and G. (II) Immunocytochemical staining of undifferentiated hESC colonies after 32 passages in four cell lines (A) AP, (B) SSEA-1, (C) SSEA-4, (D) TRA-1-60 and (E) TRA-1-81. Bar = 100 µm.