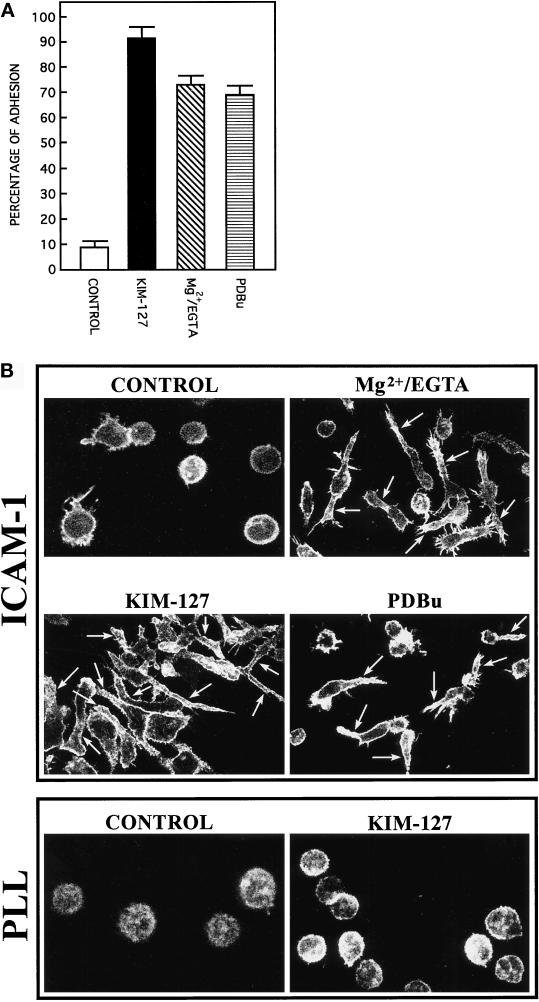
Figure 1.
Agents that activate LFA-1 integrin cause an increment in adhesion and polarization of lymphoblasts. (A) T lymphoblasts plated on ICAM-1-Fc–coated plastic dishes were allowed to adhere for 60 min in the absence (CONTROL) or the presence of different of LFA-1–activating agents: 10 μg/ml mAb KIM-127 (KIM-127), 10 mM Mg2+ plus 1 mM EGTA (Mg2+/EGTA), and 50 nM PDBu. Cell adhesion assays were carried out as specified in MATERIALS AND METHODS. The results are the mean ± SEM of four independent experiments. (B) T lymphoblasts were plated either on ICAM-Fc–coated dishes (ICAM-1) or on poly-l-lysine–coated dishes (PLL) and stimulated as indicated above. The cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with Texas Red–conjugated phalloidin. Immunofluorescence was analyzed by confocal laser microscopy as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. Arrows indicate the position of the cellular extensions in representative polarized cells.