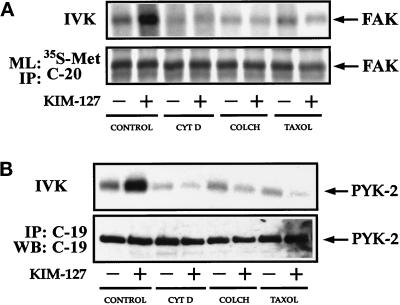
Figure 10.
Cytoskeletal interfering agents block LFA-1–dependent increase in FAK and PYK-2 kinase activities. (A) T Lymphoblasts were washed in RPMI 1640 medium and then pretreated for 4 h with 0.3% DMSO (CONTROL), with 2.5 μM cytochalasin D dissolved in DMSO (CYT D), with 10 μM colchicine dissolved in DMSO (COLCH), or with 1 μM taxol dissolved in DMSO (TAXOL). T cells were subsequently plated onto ICAM-1-Fc–coated dishes and allowed to adhere for 60 min in the absence (−) or presence (+) of 10 μg/ml mAb KIM-127. Cells were lysed, and lysates were incubated with the C-20 antibody to immunoprecipitate FAK. Kinase activities in the resulting immunoprecipitates were measured by in vitro kinase reactions performed as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS (IVK, top). FAK levels were determined in parallel cultures by metabolic labeling the cells with [35S]methionine and immunoprecipitation of the labeled extracts with C-20 antibody (ML: 35S-Met and IP: C-20, bottom). The position of FAK is indicated with an arrow. (B) T Lymphoblasts were pretreated as in A in the presence of DMSO (CONTROL), cytochalasin D (CYT D), colchicine (COLCH), or (TAXOL). T cells were subsequently plated onto ICAM-1-Fc–coated dishes and allowed to adhere for 30 min in the absence (−) or presence (+) of 10 μg/ml mAb KIM-127. Cells were then lysed, and half of the lysates were incubated with C-19 antibody to immunoprecipitate PYK-2 and kinase reactions performed as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS (IVK, top). The other half of the lysates were also immunoprecipitated with C-19 antibody and analyzed by SDS-PAGE, followed by transfer of proteins to Immobilon membranes and Western blotting with anti-PYK-2 antibodies (IP: C-19 and WB: C-19, bottom). The position of PYK-2 is indicated with an arrow.