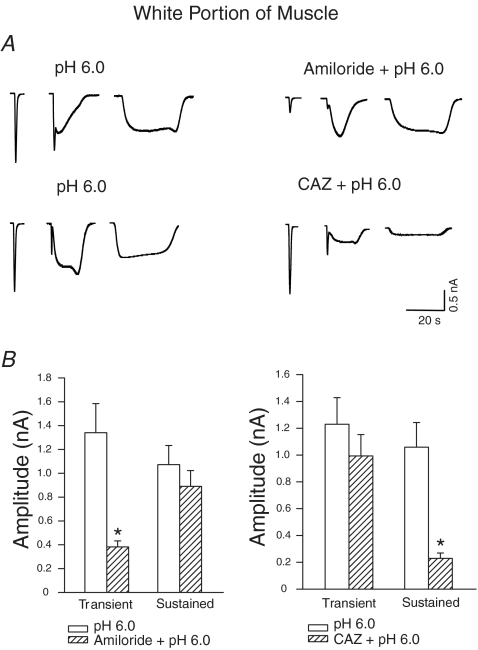
Figure 2. Effects of prior blocking of acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs) and TRPV1 capsaicin receptors with amiloride and capsazepine on acid-evoked currents in DRG neurones innervating the white portion of the gastrocnemius muscle.
A, original traces. B, amiloride attenuated the transient proton currents and the transient component of the mixed proton currents; capsazepine (CAZ) attenuated sustained proton-induced currents and the sustained part of the mixed currents. *P < 0.05, versus pH 6.0 applied alone.