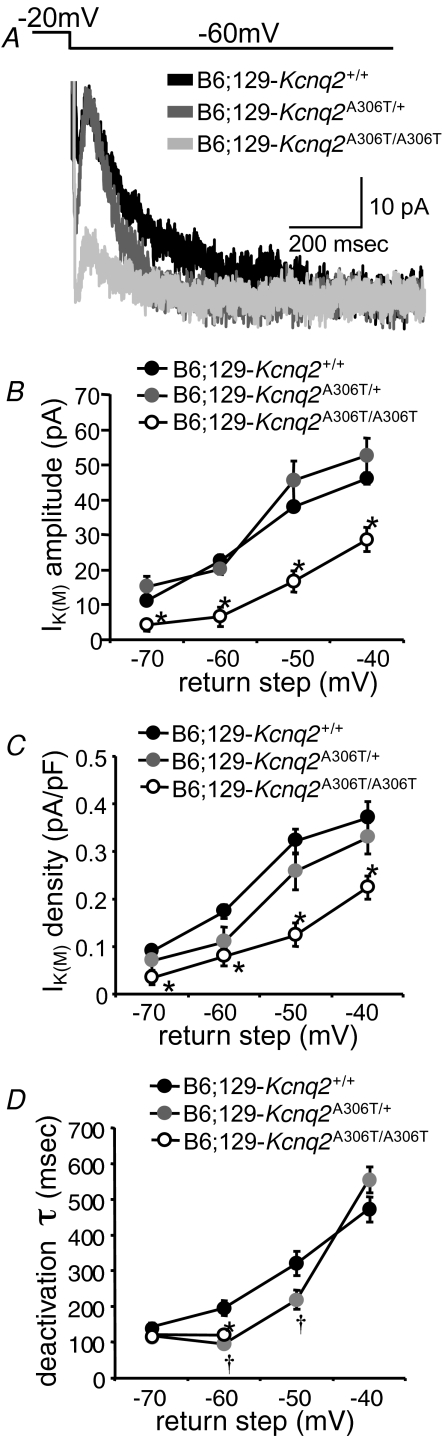
Figure 8.
IK(M) amplitude and density are decreased in B6;129 CA1 neurons carrying the Kcnq2 A306T mutation A, sample traces recorded from wild-type B6;129-Kcnq2+/+ (black), heterozygous mutant B6;129-Kcnq2A306T/+ (darker grey), and homozygous mutant B6;129- Kcnq2A306T/A306T (lighter grey) CA1 neurons in response to the −20 to −60 mV step. IK(M) amplitude is measured from the deactivation hump (10–20 ms after the hyperpolarizing step) to the steady-state level at the end of the trace. B, IK(M) amplitude is decreased relative to wild-type in B6;129-Kcnq2A306T/A306T CA1 neurons (*P < 0.001; all return steps). C, IK(M) density is also decreased in B6;129- Kcnq2A306T/A306T CA1 neurons (*P < 0.005; all return steps). D, IK(M) deactivation kinetics are faster in B6;129-Kcnq2A306T/+ CA1 neurons than wild-type at the −60 and −50 mV return step (†P < 0.05); in B6;129-Kcnq2A306T/A306T CA1 neurons, IK(M) deactivation is faster than wild-type at the −60 mV step (*P < 0.05).