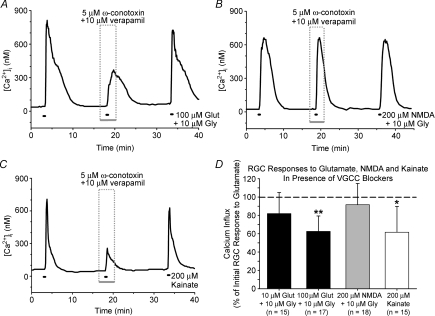
Figure 4. Effect of voltage-gated Ca2+ channel (VGCC) inhibition on glutamatergic RGC Ca2+ influx.
A–C, representative fura-2 ratio traces for RGCs treated with 100 μm glutamate (A), 200 μm NMDA (B) and 200 μm kainate (C) in the presence or absence of 5 μm ω-conotoxin GVIA and 10 μm verapamil. D, mean data (+1 s.d.) showing effects of VGCC blocking cocktail on Ca2+ influx induced by 10 μm and 100 μm glutamate, 200 μm NMDA and 200 μm kainate (extracellular Mg2+ absent; 10 μm glycine added to glutamate and NMDA solutions). Ca2+ influx was the change in [Ca2+]i due to treatment, and was normalized to the initial glutamate, NMDA or kainate responses (dashed line). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, Friedman ANOVA, Tukey, compared to initial and recovery responses.