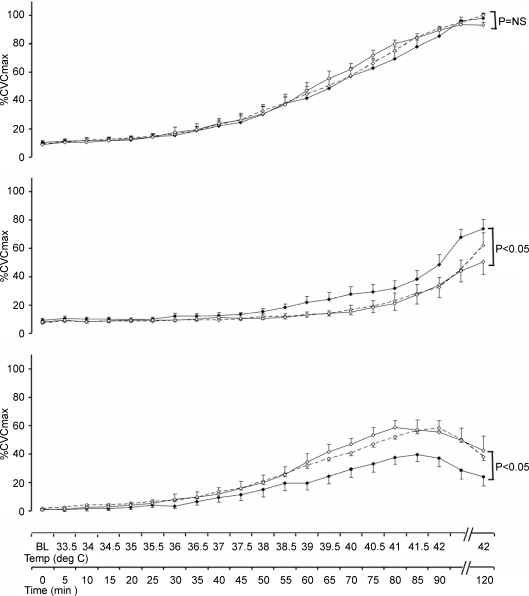
Figure 5. Effects of exercise training on heating responses: Impact of nitric oxide blockade.
The impact of 12 (◊ dashed lines) and 24 weeks (◊ continuous line) of exercise training in older sedentary subjects, compared to data collected at entry to the study (♦ continuous line), on the NO contribution to %CVC responses (lower panel), calculated for each subject at each data point by subtracting l-NAME %CVC data (middle panel) from Ringer solution %CVC data (upper panel) at the same time points and skin temperatures. Whilst training did not modify %CVC at the Ringer solution site, the impact of l-NAME and the contribution of NO to %CVC responses were significantly greater after training (P < 0.05) at both 12 and 24 weeks. This abolished the initial difference that existed between the old sedentary and older fit subjects (see Fig. 2).