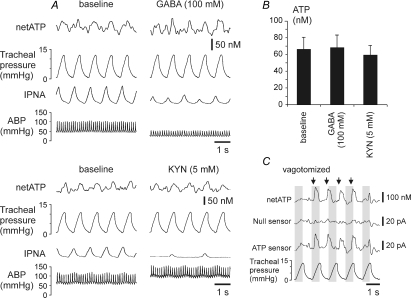
Figure 5. ATP release in the NTS is not affected by the blockade of excitatory amino acid receptors or activation of GABA receptors and can be evoked by electrical stimulation of the vagus nerve.
A, raw data showing recordings of the arterial blood pressure, phrenic nerve activity, tracheal pressure and difference in current between ATP and null sensors in basal conditions and during applications of EAA receptor antagonist kynurenic acid (KYN) or GABA on the exposed dorsal surface of the brainstem. B, mean amplitudes of the rhythmic ATP signal following applications of kynurenic acid or GABA on the dorsal surface of the brainstem (n = 4). C, electrical stimulation of the vagus nerve triggers release of ATP in the NTS. Arrows indicate the onset of 250 ms stimulation period. ABP, arterial blood pressure; IPNA, integrated phrenic nerve activity (arbitrary units).