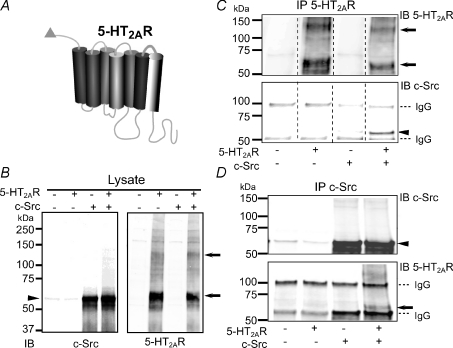
Figure 5. Association of 5-HT2AR and c-Src in cotransfected HEK 293T cells.
A, diagram of 5-HT2AR with c-Myc tag (triangle) at the N-terminus. B, immunoblot (IB) showing the expression of c-Src (left panel, anti-c-Src mAb) and 5-HT2AR (right panel, anti-c-Myc pAb) in lysates of cells transfected or not with 5-HT2AR ± c-Src. Thirty micrograms of total protein was loaded in each lane. C, IP of 5-HT2AR (with anti-c-Myc mAb) immunoblotted (IB) for 5-HT2AR (with anti-c-Myc pAb; top) and for c-Src (with anti-c-Src mAb; bottom). Only when both proteins were coexpressed, IP of 5-HT2AR pulled down c-Src (bottom panel, last lane). D, reverse co-IP using anti-c-Src mAb for IP. Immunoblots were probed with anti-c-Src pAb (top) and anti-c-Myc mAb for 5-HT2AR (bottom). The 5-HT2AR co-immunoprecipitates with c-Src only when both proteins are coexpressed (bottom panel, last lane). In all panels, arrows mark 5-HT2AR immunosignals with apparent molecular masses of ∼60–62 and ∼125–128 kDa that would correspond to mature monomeric and dimeric forms of the receptor. A faint band at ∼51–55 kDa (B and C) could be the immature form of the 5-HT2AR. Arrowheads mark c-Src signal at ∼60 kDa. Immunoglobulin G is marked with a dashed line. Three independent experiments were performed in each set of conditions. Concentrations of Abs are given in the Methods.