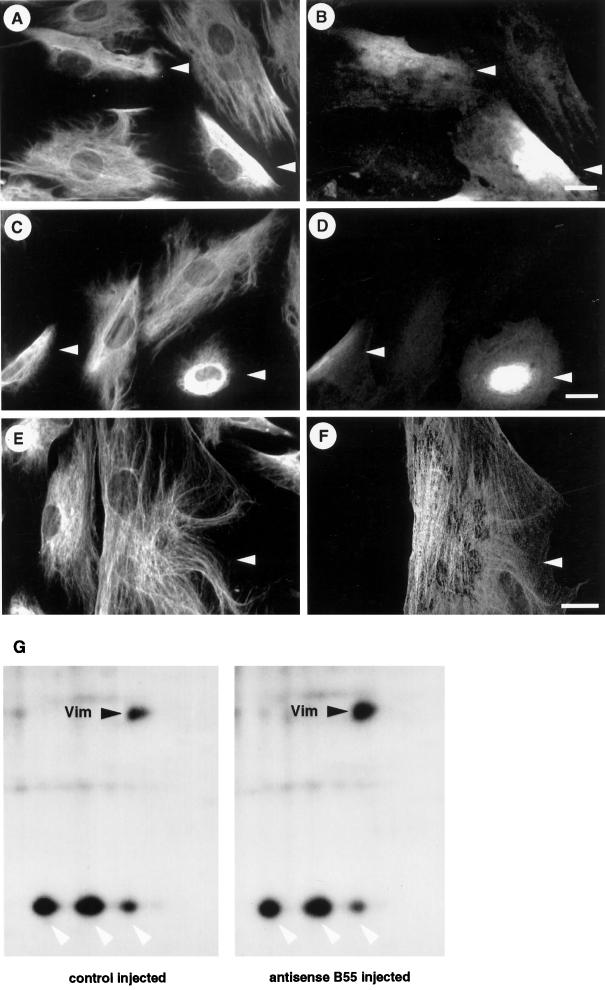
Figure 4.
Vimentin disassembly and hyperphosphorylation after the functional knockout of B55. (A–D) Hs68 fibroblasts were microinjected with pECE-B55as and cultured for 6 h (A and B) or 12 h (C and D). Cells were then stained for vimentin (A and C). Arrowheads indicatemicroinjected cells as identified by costaining against the marker antibody (B and D). (E and F) Similarly, Hs68 fibroblasts were microinjected with a B56 antisense construct (manuscript in preparation) and subsequently stained for vimentin (E) and injection marker (F). Note that antisense B56 did not induce any changes in vimentin integrity. Bars, 5 μm. (G) Hs68 fibroblasts were grown on 1-mm2 glass chips and microinjected with the control plasmid pECE or the antisense B55-expressing construct pECE-B55as. Cells were subcultured for 6 h and then metabolically labeled with [32P]H3PO4 for 3 h. Subsequently, phosphoproteins were analyzed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. Shown are portions of the autoradiograms containing vimentin (black arrowheads) and surrounding proteins only (white arrowheads indicate hsp 28). Shown are phosphoproteins of 230 cells injected with the control plasmid pECE (left panel) and 216 cells injected with the antisense B55 construct pECE-B55as (right panel). Autoradiographs were exposed for 4 d at −80°C and quantitated using a PhosphorImager.