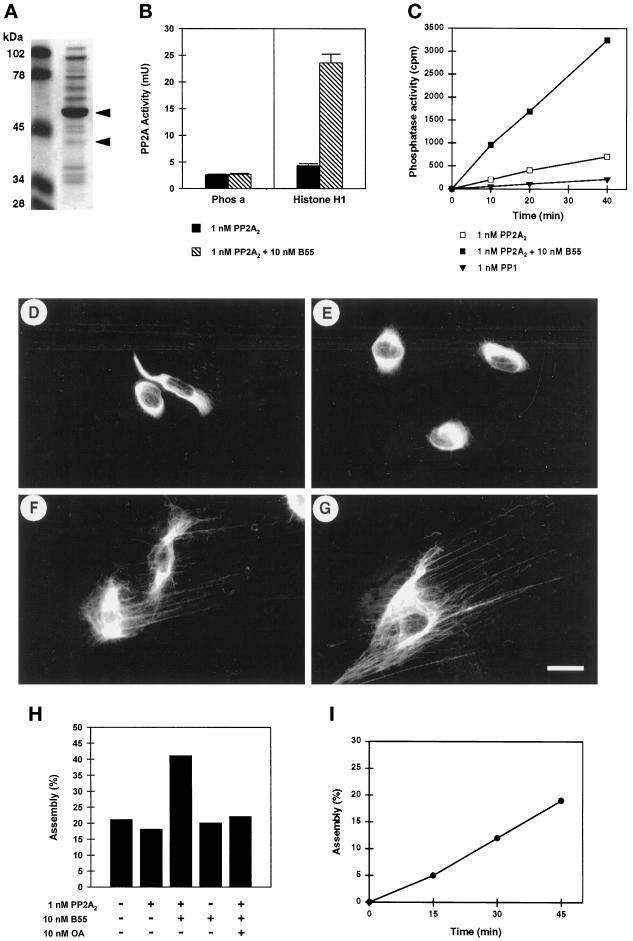
Figure 6.
Enhanced dephosphorylation of vimentin in the presence of recombinant B55. (A) Twenty microliters of recombinant B55 prepared as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS were electrophoretically separated, and proteins were visualized using Coomassie brilliant blue. The molecular masses of marker proteins in kilodaltons (lane M) are indicated at the left. The major full-length and minor proteolytically degraded forms of B55, as identified by immunoblotting, are indicated with arrowheads. (B) The effect of B55 on the activity of purified dimeric PP2A2 toward phosphorylase and (p34cdc2 phosphorylated) histone H1 was assayed. Before the assay, PP2A2 (at 1 nM final concentration) was preincubated with (black bars) or without (hatched bars) ∼10 nM (final) recombinant B55 on ice. (C) Nitrocellulose strips, containing hyperphosphorylated [32P]vimentin were prepared as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. Similarly to the phosphatase assays shown in B, strips containing equal amounts of [32P]vimentin (∼30,000 cpm and 5 μg of protein) were incubated with either 1 nM dimeric PP2A2 preincubated with (open squares) or without (closed squares) 10 nM recombinant B55 or with 1 nM catalytic subunit of PP1 (triangles). Phosphate release was determined and plotted against the assay time. (D–I) Hs68 fibroblasts grown on coverslips were treated with 1 μM OA for 1 h. Soluble proteins were extracted using Triton X-100 and 1.5 M KCl, and the remaining vimentin lattices were extensively washed in phosphatase assay buffer. Subsequently coverslips were overlaid with 30 μl of protein phosphatase assay buffer containing no phosphatase (D), 1 nM PP2A2 (E), or 1 nM PP2A2 and ∼10 nM recombinant B55 (F and G) and incubated at 37°C for 45 min. Reactions were stopped by formalin fixation and further stained for vimentin distribution. Bar, 5 μm. (H) Quantitative representation of the experiment shown in D–G; vimentin distribution resembling D or E was counted as bundled, whereas that resembling F or G or Figure 1B, upper left (unaffected vimentin), was counted as (re)assembled. On average, 600 stained vimentin lattices of each coverslip (i.e., assay point) were counted. In all assays ∼20% of the vimentin lattices had normal appearance and had not been affected by the initial OA treatment. (I) Time course of vimentin dephosphorylation by 1 nM PP2A2 and 10 nM B55. Vimentin reassembly was determined as in H, and for each time point the corresponding background (no PPase) was subtracted.