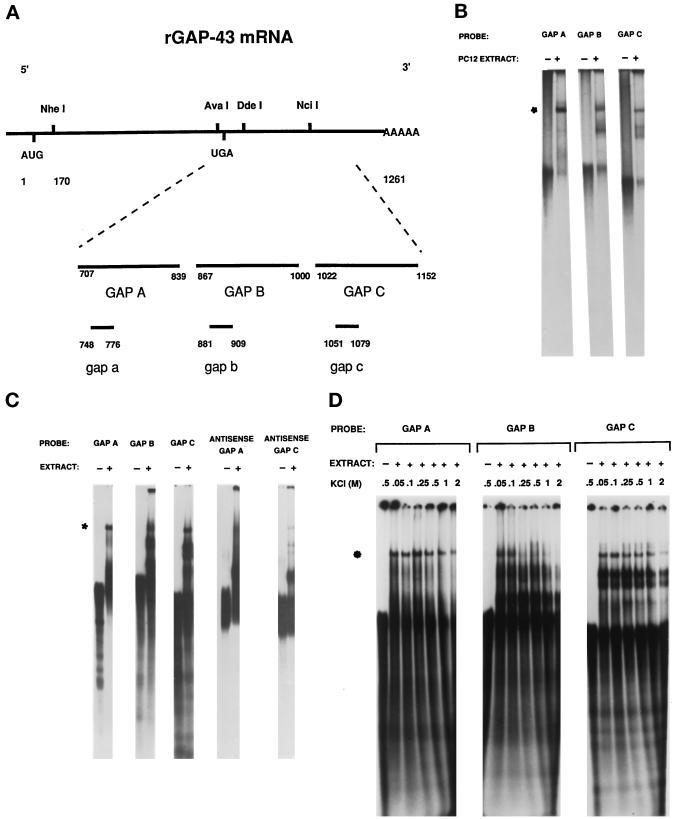
Figure 2.
RNA–protein complex 1 forms with many RNA species over a range of salt concentrations. (A) The map of rat GAP-43 mRNA indicates the location of the GAP A, GAP B, GAP C, gap a, gap b, and gap c RNA probes used in RNA mobility shift assays. The numbering is according to Basi et al. (1987). The translational stop codon, UGA, is located at sequence number 731. (B) Radiolabeled GAP A, GAP B, and GAP C were incubated with extracts from 16-h NGF-treated PC12 cells and electophoresed through a 6% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel. The asterisk indicates a common, comigrating RNA–protein complex (complex 1) that formed with each RNA molecule. (C) Radiolabeled GAP A, GAP B, GAP C, antisense GAP A, and antisense GAP C were incubated with brain protein extract and electrophoresed through a 6% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel. The asterisk indicates complex 1 formed with each probe. (D) Radiolabeled GAP A, GAP B, and GAP C RNA probes were incubated with brain protein extract in the presence of increasing amounts of KCl and electrophoresed through a 6% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel. The asterisk indicates complex 1.