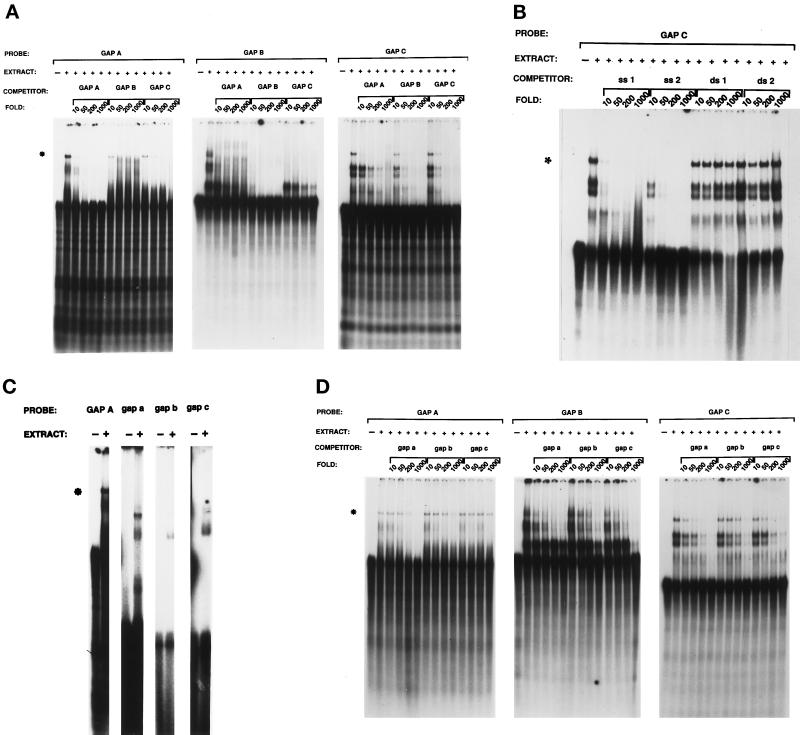
Figure 3.
Complex 1 forms with single-stranded RNA in a sequence-insensitive and size-dependent manner. (A) Complex 1 forms in a relatively sequence-insensitive manner. Excess nonradiolabeled GAP A, GAP B, and GAP C were added, at the indicated molar concentrations, to binding reactions containing brain protein extract and the GAP A, GAP B, or GAP C RNA probes. (B) Complex 1 forms with single-stranded, but not double-stranded, RNA. Excess random RNA polymers were added at the indicated molar concentrations to binding reactions containing brain protein extract and the GAP C RNA probe, where ss 1 represents single stranded polyadenylic-guanylic-uridylic acid (AGU); ss 2, single-stranded polycytidylic-inosinic-uridylic acid (CIU); ds 1, double-stranded polyadenylic-polyuridylic acid (A·U); and ds 2, double-stranded polycytidylic-polyguanylic acid (C·G). (C) Complex 1 forms in a size-dependent manner. Radiolabeled GAP A, gap a, gap b, and gap c were incubated with brain protein extract and electrophoresed through a 6% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel. Complex 1, indicated by the asterisk, is observed only with the GAP A probe. (D) Although not capable of forming complex 1, small RNAs interact with some components of complex 1 and inhibit its formation. Excess nonradiolabeled gap a, gap b, or gap c were added at the molar excess indicated to binding reactions containing brain protein extracts and GAP A, GAP B, and GAP C RNA probes. The asterisk indicates complex 1.