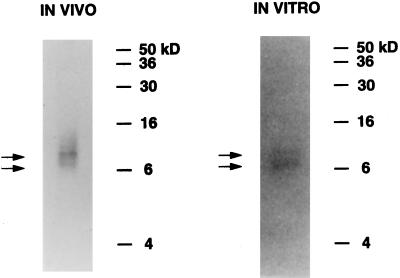
Figure 5.
V8 digestion indicates that the ∼160-kDa RNA-binding proteins identified in vivo and in vitro are highly similar. The ∼160-kDa protein was excised from the 10% SDS polyacrylamide gels used to separate the UV cross-linked RNA-binding proteins in both the in vivo and the in vitro experiments (as described in Figures 1 and 4A, respectively). The gel slice was layered onto the stacking gel of a 17.5% SDS polyacrylamide gel along with S. aureus V8 protease. Digestion by S. aureus V8 protease occurred in situ during a pause in electrophoresis through the stacking gel. Radiolabeled peptide fragments ∼7 kDa and ∼9 kDa (arrows) were obtained from V8 digestion of both the ∼160-kDa RNA-binding proteins found in vivo and in vitro. As explained in the text, the fact that the radiolabeled RNA probes used for the in vivo experiment (total cellular mRNA) and the corresponding in vitro experiment (GAP A) are different makes it unlikely that the number of radioactive U nucleotides in the RNA fragments cross-linked to the two V8 digestion fragments would be equal in the two experiments. Only the equal size of the fragments is relevant to the question of whether the two 160-kDa proteins are similar.