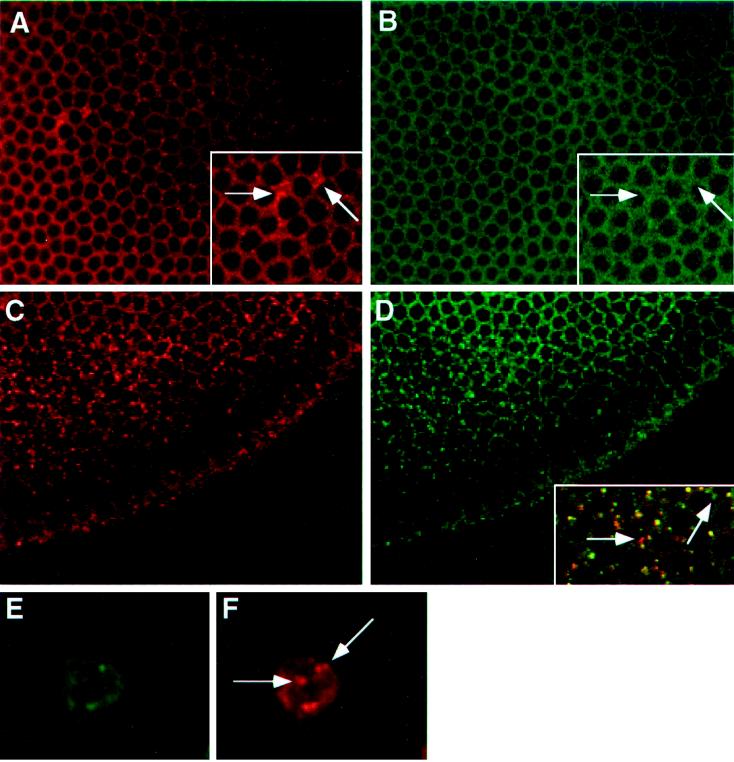
Figure 5.
Immunofluorescent localization of Delta extracellular and intracellular domains in cellular blastoderm embryos, and in cultured cells programmed to express DeltaWTNdeMYC. (A) Cellular blastoderm stained with MAb9B to the Delta extracellular domain. (B) Same embryo as in panel A, showing localization of the Delta intracellular domain (C2 guinea pig polyclonal antisera). Insets in panels A and B, a section of the larger panel presented at higher magnification, illustrate the difference between the localization of Delta extracellular and intracellular domains (arrows). (C) Cellular blastoderm embryo, immediately before gastrulation, showing localization of the Delta extracellular domain detected with MAb9B. At this stage, Delta is plasma membrane-associated, except in the mesodermal anlage where Delta accumulates in vesicles. (D) Same embryo as in panel C, showing localization of the Delta intracellular domain with C2 guinea pig polyclonal antisera. Inset in panel D shows a high magnification, merged image of the same area of panels C and D, to illustrate that Delta extracellular and intracellular domains colocalize in vesicular structures. However, some vesicular structures react with only one of the two domain-specific antibodies (arrows). (E and F) A cultured cell programmed to express DeltaWTNdeMYC. The Delta extracellular domain is detected with GP581 guinea pig polyclonal antiserum in panel E, and localization of the intracellular domain is assessed with MAb9E in panel F. Arrows in panel F indicate vesicles that reacts only with MAb9E.