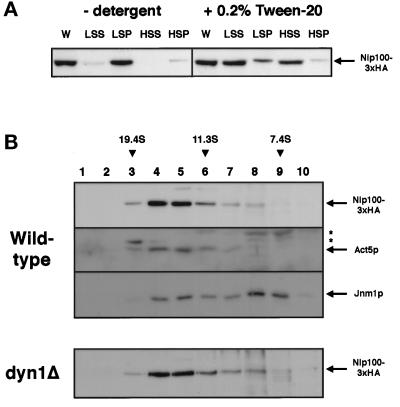
Figure 5.
Biochemical characterization of the yeast dynactin complex. (A) Detergent solubility of Nip100-3xHA from whole-cell extracts. Cells expressing Nip100-3xHA were lysed in buffer with or without 0.2% Tween 20 nonionic detergent. The lysate was spun at 13,000 rpm in a microcentrifuge, and the low-speed supernatant was then spun at 55,000 rpm (∼100,000 × g) in a tabletop ultracentrifuge. Equal fractions of the whole-cell extract (W), low-speed supernatant (LSS), low-speed pellet (LSP), high-speed supernatant (HSS), and high-speed pellet (HSP) were analyzed by immunoblotting with the 12CA5 anti-HA monoclonal antibody. (B) Sucrose density gradient centrifugation indicates that Nip100p, Act5p, and Jnm1p are all present in a 15.5S complex, which does not include cytoplasmic dynein. High-speed supernatants from wild-type or dyn1Δ strains expressing Nip100-3xHA were analyzed in 7–18% sucrose gradients. Ten equal fractions were collected and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using antibodies against the HA tag (wild-type panel, top row; and dyn1Δ panel), Act5p (wild-type panel, second row), and Jnm1p (wild-type panel, third row). Cross-reacting bands detected by the antiAct5p antibody are denoted with an asterisk. Purified thyroglobulin (19.4S), catalase (11.3S), and yeast alcohol dehydrogenase (7.4S) were used as standards.