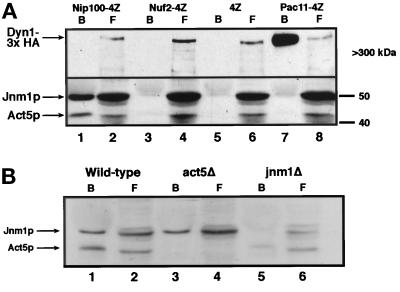
Figure 6.
Direct biochemical interactions between dynactin homologues and dynein chains. Cells expressing HA-tagged Dyn1p (Dyn1-3xHA) and various protein A IgG binding site (4Z)–tagged proteins were lysed under nondenaturing conditions, and the extracts were incubated with human IgG-Sepharose beads. After washing, bound (B) and free (F) proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and blotted to nitrocellulose. Blots were probed with antibodies against Act5p, Jnm1p, and the HA tag. The bound fractions were concentrated 10-fold (with respect to free fractions) before electrophoresis. (A) Act5p and Jnm1p specifically coprecipitate with Nip100-4Z (lanes 1 and 2) but not with Nuf2-4Z (lanes 3 and 4), 4Z (lanes 5 and 6), or Pac11-4Z (lanes 7 and 8). Note that Act5p migrates at the expected 42 kDa, whereas Jnm1p (predicted molecular mass, 43.6 kDa) migrates at ∼50 kDa. The heavy chain of cytoplasmic dynein (Dyn1-3xHA) specifically coprecipitates only with the intermediate chain (Pac11-4Z). (B) Wild-type (lanes 1 and 2), act5Δ (lanes 3 and 4), and jnm1Δ (lanes 5 and 6) cells expressing Nip100-4Z were processed as in A. Although the absence of Act5p has no effect on Jnm1p binding to Nip100-4Z, there is a 5- to 10-fold decrease in binding of Act5p to Nip100-4Z in a jnm1Δ strain.