Abstract
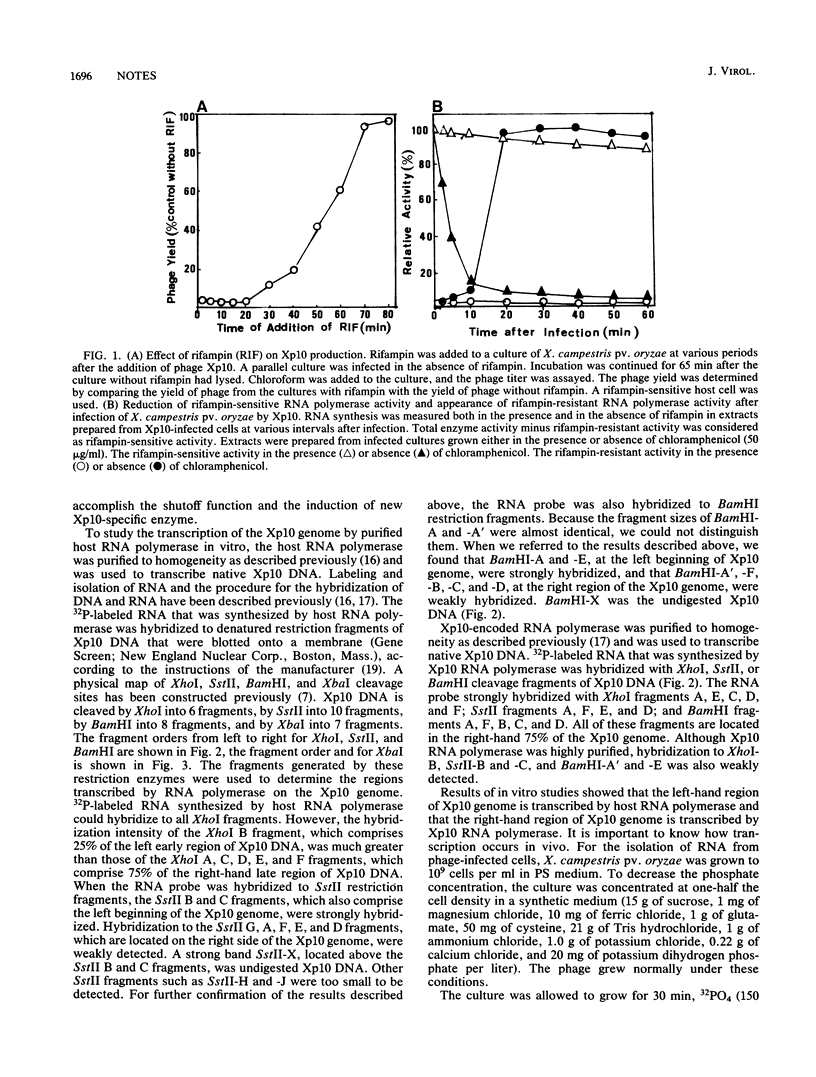
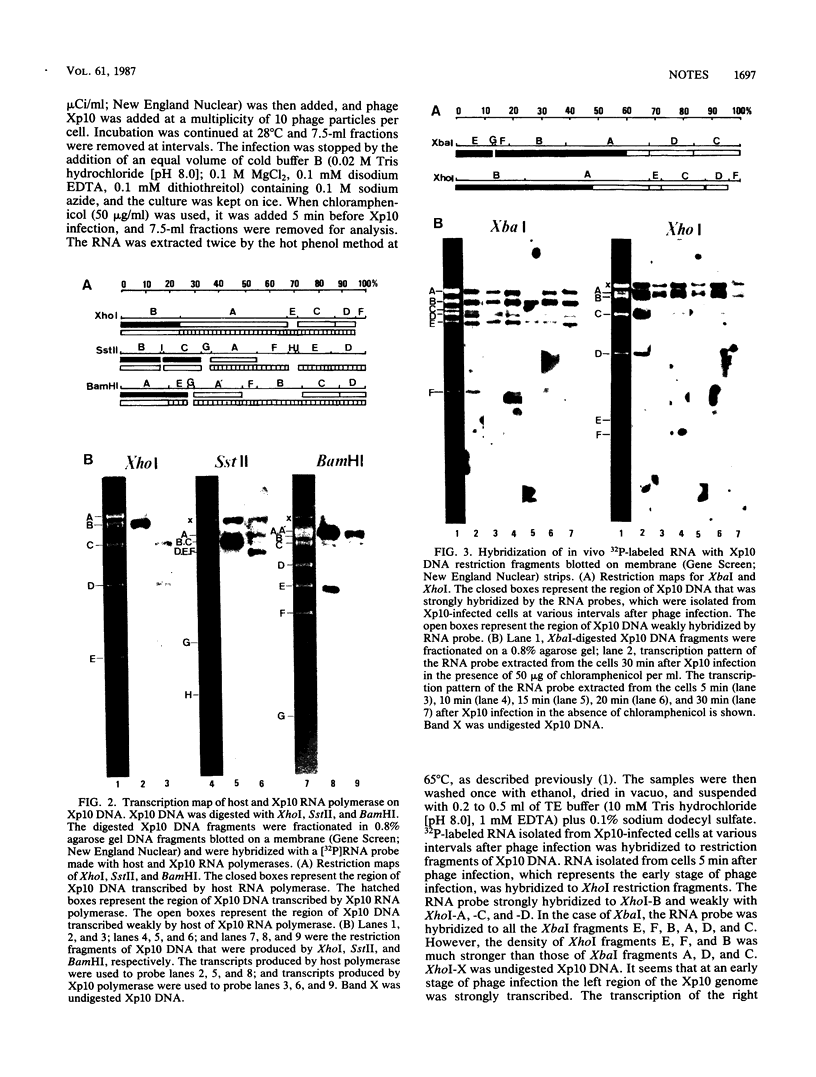
Results of in vivo studies showed that the transcription of the Xp10 genome in Xp10-infected cells shifted from rifampin sensitivity to rifampin resistance. Results of in vitro studies showed that a rapid reduction of rifampin-sensitive RNA polymerase activity coincided with a rapid increase of rifampin-resistant RNA polymerase activity in cell extracts with time after infection. Host and Xp10-encoded RNA polymerases were purified, and the transcripts from these two enzymes were hybridized to the restriction fragments of Xp10 DNA. The RNA probe generated by host RNA polymerase hybridized strongly to the leftmost 25% of Xp10 DNA and weakly to the rightmost 75% of Xp10 DNA. The RNA probe generated by Xp10 RNA polymerase hybridized strongly to the rightmost 75% of Xp10 DNA and weakly to the leftmost 25% of Xp10 DNA. Studies with 32P-labeled RNA isolated at various intervals after infection did not reveal any evidence for early versus late differences in transcription.
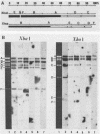
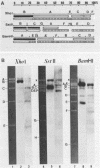
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amemiya K., Shapiro L. In vitro transcription of the early region of Caulobacter phage phi Cd1 deoxyribonucleic acid by host RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 14;21(19):4707–4713. doi: 10.1021/bi00262a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler E. T., Chamberlin M. J. Bacteriophage SP6-specific RNA polymerase. I. Isolation and characterization of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5772–5778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty P. R., Sarkar P., Huang H. H., Maitra U. Studies on T3-induced ribonucleic acid polymerase. 3. Purification and characterization of the T3-induced ribonucleic acid polymerase from bacteriophage T3-infected Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6637–6646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M., McGrath J., Waskell L. New RNA polymerase from Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T7. Nature. 1970 Oct 17;228(5268):227–231. doi: 10.1038/228227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M., Ring J. Characterization of T7-specific ribonucleic acid polymerase. 1. General properties of the enzymatic reaction and the template specificity of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2235–2244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S., Losick R., Pero J. New RNA polymerase from Bacillus subtilis infected with phage PBS2. Nature. 1974 Nov 1;252(5478):21–24. doi: 10.1038/252021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. Transcriptional specificity of a multisubunit RNA polymerase induced by Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage PBS2. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):224–237. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.224-237.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., McAllister W. T., Bautz E. K. In vitro transcription of T3 DNA by Escherichia coli and T3 polymerases. Virology. 1972 Apr;48(1):112–125. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90119-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falco S. C., Zehring W., Rothman-Denes L. B. DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from bacteriophage N4 virions. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4339–4347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falco S. C., Zivin R., Rothman-Denes L. B. Novel template requirements of N4 virion RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3220–3224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolly J. F. Program of bacteriophage gh-1 DNA transcription in infected Pseudomonas putida. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):771–776. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.771-776.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Butler E. T., Roulland D., Chamberlin M. J. Bacteriophage SP6-specific RNA polymerase. II. Mapping of SP6 DNA and selective in vitro transcription. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5779–5788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao Y. D., Kuo T. T. Loss of sigma-factor of RNA polymerase of Xanthomonas campestris pv. oryzae during phage Xp10 infection. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13714–13719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister W. T., McCarron R. J. Hybridization of the in vitro products of bacteriop&hage T7 RNA polymerase to restriction fragments of T7 DNA. Virology. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):288–298. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. C., Siegel R. B. Transcription of late phage RNA by T7 RNA polymerase. Nature. 1970 Dec 19;228(5277):1160–1162. doi: 10.1038/2281160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towle H. C., Jolly J. F., Boezi J. A. Purification and characterization of bacteriophage gh-I-induced deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase from Pseudomonas putida. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1723–1733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehring W. A., Rothman-Denes L. B. Purification and characterization of coliphage N4 RNA polymerase II activity from infected cell extracts. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8074–8080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]