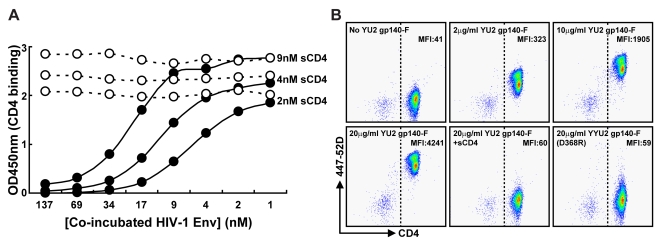
Figure 1. Soluble Env trimers bind to soluble and cell-surface CD4.
(A) sCD4 at concentrations of 2, 4 and 9 nM was co-incubated with YU2 gp140-F trimers (filled circles) or CD4-binding-defective gp140 368D/R trimers (open circles) at concentrations shown. Subsequently, non-trimer-bound sCD4 was captured in an ELISA format by the anti-CD4 antibody RPA-T4, competing with HIV-1 Env for CD4 binding. RPA-T4-captured sCD4 was detected with the non-competing anti-CD4 antibody, OKT-4 and plotted as shown. (B) Cynomolgus macaque PBMCs were incubated with 2, 10 or 20 µg/ml of YU2 gp140-F trimers, 20 µg/ml gp140-F trimers in the presence of an excess sCD4 (100 µg/ml) or with 20 µg/ml of gp140-F 368D/R trimers. Cells were stained for CD3, CD4 and CD8 expression and analyzed by flow cytometry. The CD3+/CD8− populations are shown (see supplemental FigS2 for gating strategy). The y-axis indicates Env binding, as detected with mAb 447-52D, and the x-axis shows CD4 expression. The CD4+ cell population was defined as cells detected to the right of the dotted line. The median fluorescence intensity (MFI) of Env binding to the CD3+/CD4+/CD8− cell population is shown.