Figure 9.
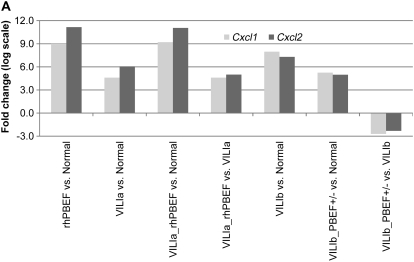
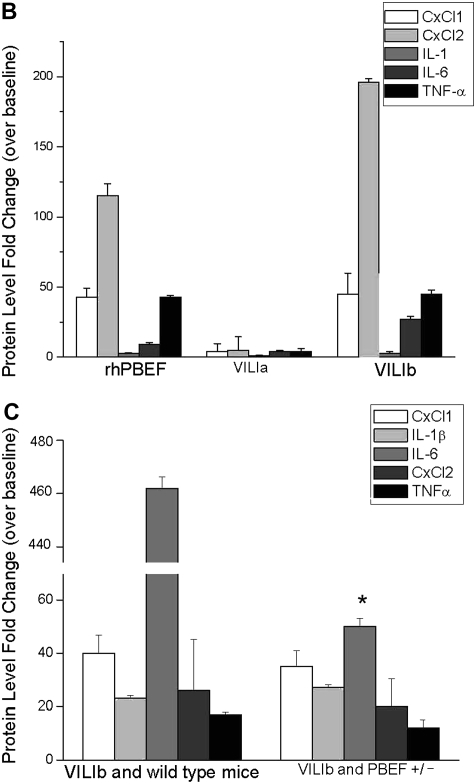
Validation of potential ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) biomarkers in lung tissue and in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid. (A) Two markers, Cxcl1 and Cxcl2, were selected by their presence across all gene lists (Table E2) (except list 5 for dysregulated genes in heterozygous pre–B-cell colony enhancing factor [PBEF+/−] mice). The levels of each gene mirrored the severity of VILI and/or the injury produced by VILI and recombinant human PBEF (rhPBEF) challenges, suggesting that Cxcl1 and Cxcl2 represent potential biomarkers in VILI. (B) VILIa- and rhPBEF-mediated challenge of wild-type B6 mice each induced significantly increased fold changes in CxCl1, CxCl2, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α compared with spontaneously breathing controls (*P < 0.05) in BAL. Moreover, the combined challenge of VILIa-rhPBEF indicated an additive effect on the induction of these cytokines (*P < 0.05). (C) Exposure of wild-type B6 mice to VILIb induced significantly elevated fold changes in CxCl1, CxCl2, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α relative to VILIb-PBEF+/− mice. Reductions in BAL cytokine production in VILIb-PBEF+/− mice are significant with IL-6 (*P < 0.05).