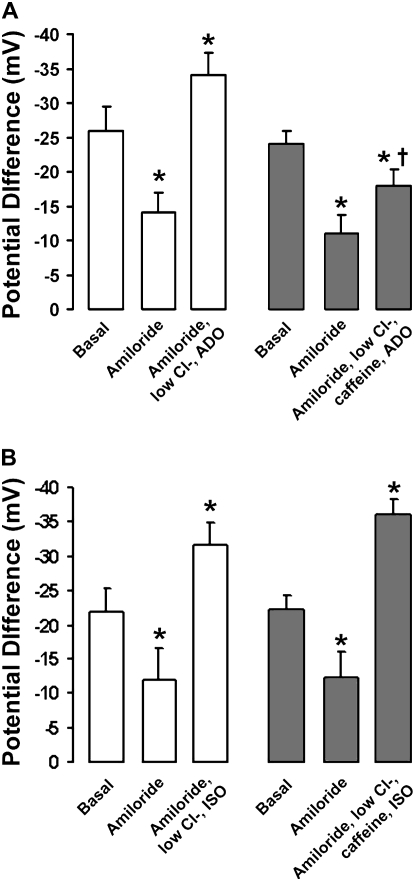
Figure 2.
ADO-R blockade inhibits cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) activation in vivo. (A) Bar graph of mean nasal potential differences (PDs) under basal conditions and after sequential exposure to 100 μM amiloride followed by amiloride with a low Cl- Ringer and 10 μM ADO (open bars), or amiloride with a low Cl- Ringer, 10 μM ADO, and 30 μM caffeine (shaded bars) (n = 6 subjects). (B) Mean nasal PDs under basal conditions, with amiloride and amiloride with a low Cl- Ringer and 10 μM isoproterenol (ISO; open bars) and with ISO and 30 μM caffeine (shaded bars) (n = 5 subjects). Data shown as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 different from basal PDs. †P < 0.05 different from ADO alone.