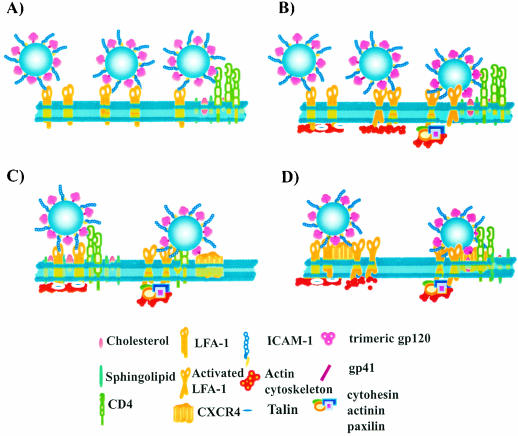
FIG. 8.
Proposed hypothetical models to explain how insertion of host ICAM-1 within HIV-1 results in an enhancement of virus attachment-fusion-internalization and cytosolic delivery. (A) Rolling of virus entity onto the cell surface due to the association between ICAM-1 and LFA-1 allows achievement of a sufficient number of interactions between gp120 and CD4. (B) Binding of virus-associated ICAM-1 to cell surface LFA-1 triggers activation of LFA-1, leading ultimately to a displacement of LFA-1 and thus of associated viruses toward lipid rafts that contain CD4. (C) Attachment of ICAM-1-bearing viruses to the surfaces of LFA-1-expressing cells can result in intracellular signal transduction events that facilitate interactions with the appropriate chemokine coreceptor. (D) A complex made of LFA-1 and CXCR4 can move into raft microdomains following binding of ICAM-1-bearing virions, leading to colocalization with CD4.