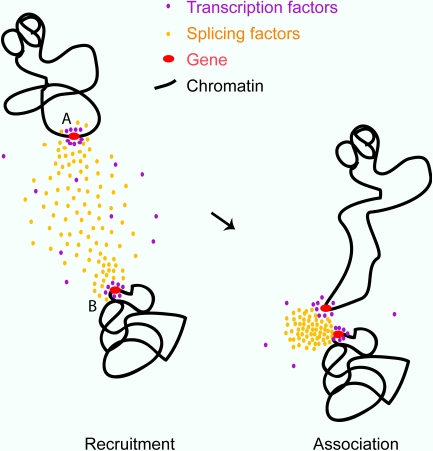
Figure 9.
A model for involvement of splicing factor aggregations in the stochastic association of transcriptionally active genes. Genes in the process of transcriptional elongation accumulate splicing-related factors (left). Nuclear speckles are known to form as concentrations of such factors in early G1 and randomly during interphase. This process of nucleation may pull more mobile chromatin (around gene A) into association with other active genes (gene B; right).