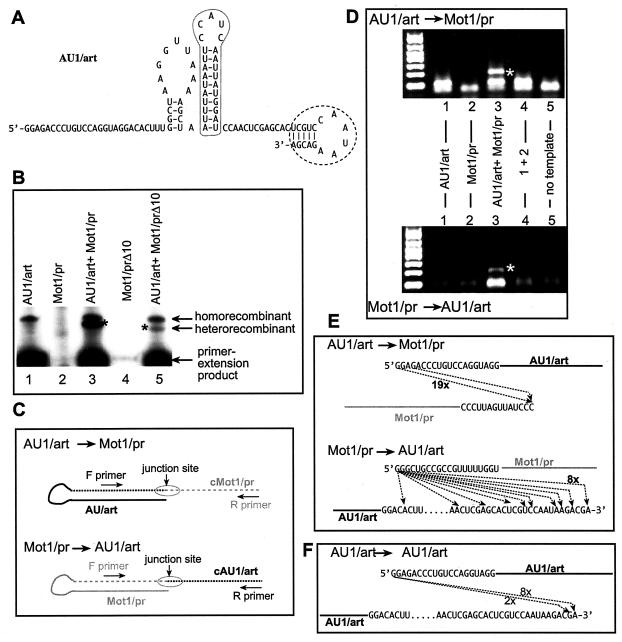
FIG. 3.
Increasing the efficiency of heterorecombinant formation by TCV RdRp. (A) A 5-bp primer sequence (named art5; encircled with dotted line) was used to replace the cPR11 sequence at the 3′ end of AU1 (Fig. 1) to increase the efficiency of primer extension by the TCV RdRp (10). (B) Denaturing gel analysis of the TCV RdRp products. The positions of the primer extension products and the putative homo- and heterorecombinants are marked on the right. The amount of Mot1/pr RNA was reduced to 0.1 μg to inhibit homorecombinant formation (Fig. 2). Construct Mot1/prΔ10 is derived from Mot1/pr (Fig. 1) by deletion of 10 nt from the 3′ end. (C) Schematic representation of the strategy used for the RT-PCR analysis of the heterorecombinants (see also panel D). Two different sets of primers were used to detect the heterorecombinants formed (depending on which template was used as a donor during the recombination events). Note that the dotted lines represent the newly synthesized RNA strands, which are complementary to the original templates (as indicated by the letter c in front of the names of the RNAs). (D) RT-PCR analysis of the putative recombinants. After the TCV RdRp reactions, the RdRp products migrating slower than the primer extension products were gel isolated and used for RT-PCR. The band representing heterorecombinants (lane 3) is marked with an asterisk. (E) Sequence analysis of the junction sites in the heterorecombinants. After the RT-PCR analysis, the bands representing the heterorecombinants were gel isolated and cloned in E. coli, and a representative number of clones was sequenced. Arrows indicate the template switching by the recombinant TCV RdRp from the donor template (top) to the acceptor template (bottom). The frequencies of clones with identical sequences are indicated by numbers next to the lines. (F) Sequences of the homorecombinants formed between identical AU1/art templates. A strategy similar to that shown in panel C was used for RT-PCR, cloning, and sequencing of homorecombinants.