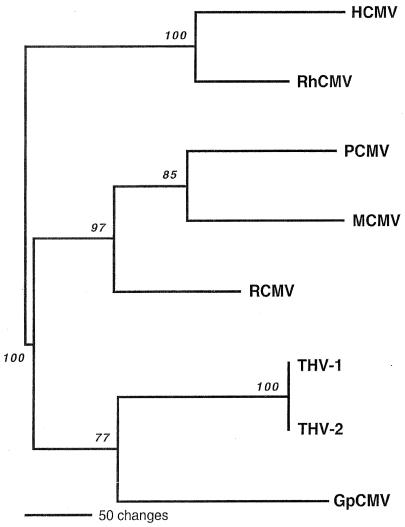
FIG. 3.
Phylogenetic relationships of PCMV to representative CMVs isolated from rodents and primates. A single most parsimonious phylogenetic tree was generated on the basis of amino acid sequence differences of the 480-amino-acid fragment of the viral DNA polymerase by using PAUP (version 4b10). Maximum-parsimony analysis was conducted by using the “branch-and-bound” search option and a “protpars” weighting matrix. Gaps were treated as “missing data.” Lengths of the horizontal branches are proportional to the amino acid step differences between corresponding taxa (see bar scale). Vertical branches are for visual clarity only. Bootstrap values obtained from 1,000 replicates of the heuristic maximum-parsimony analysis are shown in italics at the appropriate branch points. Previously published CMV DNA polymerase sequences used in the analysis include the following: HCMV strain AD169 (GenBank accession number X17403), RhCMV strain 68-1 (AF033184), MCMV strain Smith (M73549), RCMV strain Maastricht (AF232689), GpCMV strain 22122 (L25706), and tupaia herpesvirus strains 1 (THV-1; AF074327) and 2 (THV-2; AF281817).