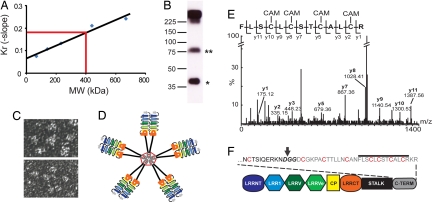
Fig. 3.
Quaternary structure of secreted VLR-B antibodies. (A) Molecular mass estimate of a purified recombinant VLR-B antibody (VLR4) by Ferguson plot analysis. Blue dots, Molecular mass standards; red line, VLR4. (B) Western blot of a partially reduced VLR-B antibody; monomeric (*) and dimeric (**) subunits of the partially reduced antibody. (C) Negative stain TEM of VLR4. (Upper) Pentameric arrangement of VLR-B subunits. (Lower) Flexibility of subunits. (D) A model of VLR-B antibody quaternary structure with red lines representing disulfide bonds. (E) MS/MS sequencing of tryptic fragments of reduced VLR4. Ions matching the sequence of the C terminus of VLR4 are labeled in the spectrograph. CAM indicates carboxyamidomethylation of cysteine by iodoacetamide. (F) Cartoon depicting the location of the cysteine-rich peptide in the VLR-B antibody. The predicted GPI cleave site (bold text) is indicated by an arrow, cysteines that may form intermolecular disulfide bonds are highlighted red, and the peptide detected in E is indicated by a line above the text.