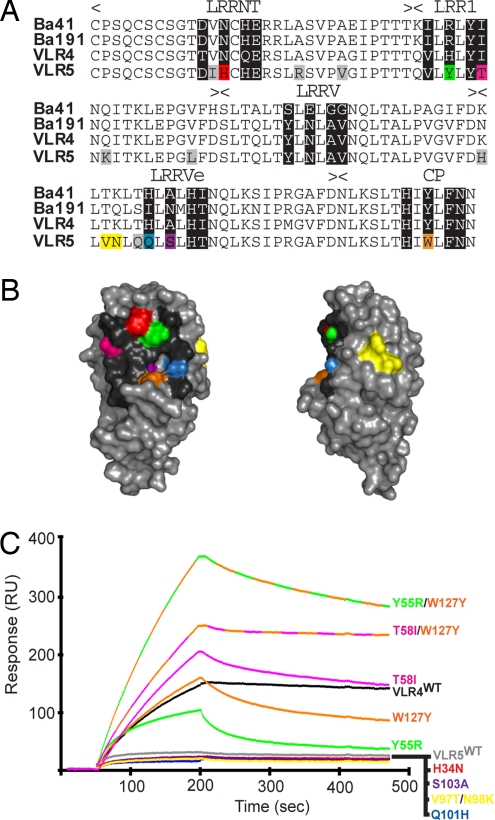
Fig. 4.
The primary antigen binding site of VLR-B is located on the concave surface. (A) Sequence alignment of high-avidity (Ba41, Ba191, VLR4) and low-avidity (VLR5) VLR-B antibodies specific for BclA-CTD. Hypervariable positions are shaded black. Amino acids in VLR5 that differ from the high-avidity clones are shaded in color if they are in hypervariable positions or gray if located elsewhere, except V97/N98 (yellow). (B) Homology-based model of VLR5 structure. Amino acids in hypervariable positions are color-coded as in A. (C) Surface plasmon resonance measurement of the interaction between VLR4WT, VLR5WT, or VLR5 mutant antibodies with BclA-CTD. VLR5 residues in hypervariable positions that differ from the high-avidity clones were mutated to the consensus amino acid of the high-avidity clones at that position. Response curves are color-coded with respect to amino acid positions depicted in A and B.