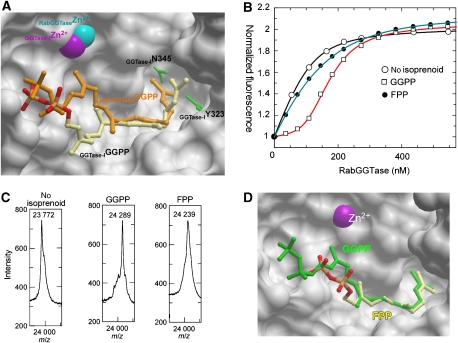
Figure 3.
Analysis of substrate specificity of RabGGTase. (A) Superimposition of structures of the RabGGTase–GGPP and GGTase-I–GGPP (1N4Q) complexes. The active site of RabGGTase is displayed in surface representation, whereas selected residues of the active site of GGTase-I are shown as green ball and stick. The ball-and-stick representation of GGPP bound to GGTase-I is displayed in atomic colours, whereas the GGPP bound to RabGGTase is coloured in orange. Zn2+ ions are displayed as CPK spheres. (B) Fluorescent titration of 200 nM mant-FPP with RabGGTase in the presence of 100 nM of different phosphoisoprenoids. The λex/em was set to 340/426 nm. The data were fitted numerically as described in the Materials and methods section, and the obtained affinities are summarized in Table II. (C) MALDI-TOF analysis of the Rab7 prenylation reaction supplemented with GGPP and FPP. In each experiment, 20 μM of Rab7, REP-1, and RabGGTase were mixed with 50 μM of the respective phosphoisoprenoid and incubated at room temperature for 30 min. (D) Superimposition of RabGGTase in complex with GGPP and FPP, displayed as in (A). GGPP is coloured in green and FPP in atomic colours.