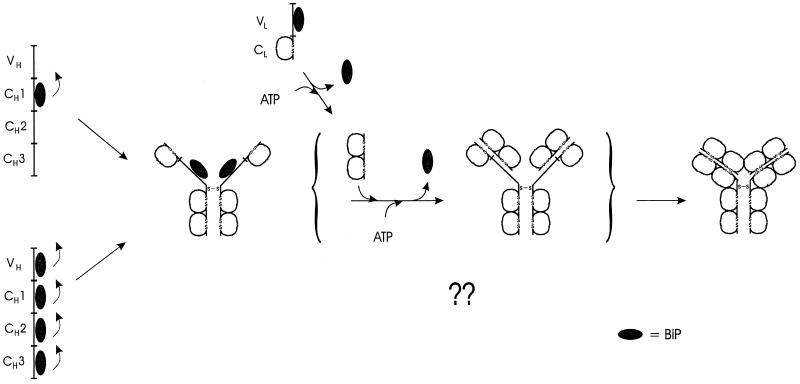
Figure 7.
Schematic of the intermediates in H2L2 Ig assembly and role of BiP in the process. Although BiP can associate transiently with other Ig heavy chain domains, the CH1 domain is the primary site of BiP binding that is responsible for the retention of unassembled heavy chains. Unlike the other heavy chain domains, the CH1 domain remains unfolded and unoxidized in the absence of LCs. Synthesis and binding of a folding competent LC to the heavy chain promotes BiP release by an undefined mechanism and allows the CH1 domain to fold. The completely folded and assembled Ig molecule is now transport competent.