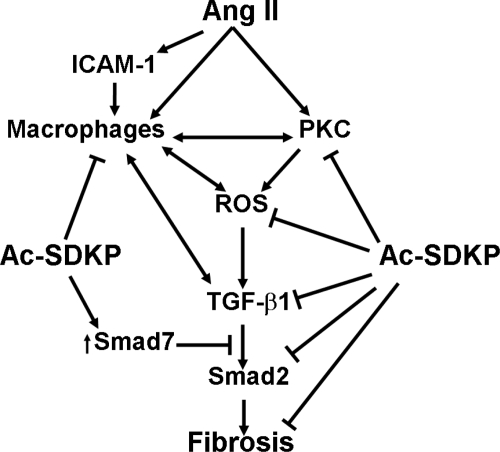
Fig. 10.
Hypothesized mechanism by which Ac-SDKP inhibits aortic fibrosis in ANG II-induced hypertension. As illustrated, ANG II activates PKC and also induces ICAM-1 expression and macrophage activation. PKC activates macrophages and also NADPH, both of which can increase reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Macrophages and ROS induce expression of TGF-β1, which, via receptor-associated Smads (Smad2 and -3), induces fibrosis. Ac-SDKP acts by decreasing PKC activation, ROS generation, macrophage infiltration, TGF-β1 expression, and inhibition of Smad2 phosphorylation. Ac-SDKP increases inhibitory Smad7, which blocks the effects of TGF-β1. Ac-SDKP may also directly inhibit fibrosis by blocking collagen synthesis and fibroblast proliferation (46).