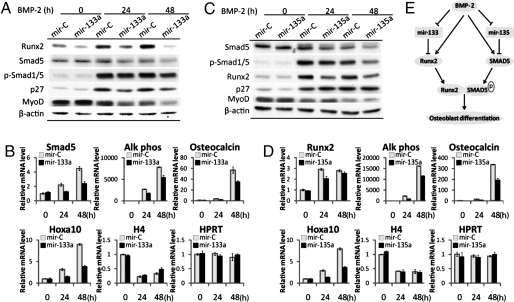
Fig. 4.
miR-133 and miR-135 inhibit BMP2-induced C2C12 osteogenic differentiation. (A) miR-133a overexpression restrained BMP2-induced Runx2, p-Smad1/5, and p27 protein increase. C2C12 cells transfected with 100 nM miR-133a and miRNA-Control (miR-C) for 12 h, then cultured in 0.25% albumin serum-free medium, which contains 300 ng/ml BMP2. Western blots for indicated proteins were performed on total cell lysates as shown. (B) miR-133 inhibits osteoblast markers Smad5, alkaline phosphatase (Alk Phos), Osteocalcin, and Hoxa10 mRNA (Q-PCR normalized by GAPDH), but has no effect on H4 and HPRT (hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase 1). (C) mir-135 down-regulates the BMP2 transducer Smad5. C2C12 cells transfected with 100 nM miR-135a were harvested and for consequences on the indicated proteins under conditions described in A. Western blots for Runx2, Smad5, p-Smad1/5, p27, MyoD, and β-actin (as control) were performed on total cell lysates as shown. (D) miR-135 decreases osteogenesis. mRNA levels of osteoblast markers Runx2, alkaline phosphatase (Alk Phos), Osteocalcin and Hoxa10, and H4 and HPRT were detected as described in B. (E) Model of miR-133 and miR-135-mediated regulation of osteoblast differentiation. MiR-133 and miR-135 targeted osteogenic factors Runx2 and Smad5, respectively. BMP2 treatment down-regulates expression of miR-133 and miR-135 and releases expression of Runx2 and Smad5 to promote osteoblast differentiation.