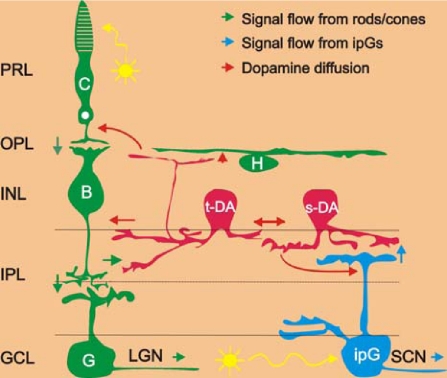
Fig. 5.
Neuronal circuit diagram of the light input pathways to dopamine cells in the mammalian retina. Blue arrows represent the light signal flow from melanopsin ganglion cells to sustained dopamine cells and the SCN; Green arrows: light signal flow from rods/cones to ganglion cells through ON-bipolar cells to transient dopamine cells and the LGN. Red arrows represent the dopamine diffusion to target cells in all retinal layers. Yellow arrows represent light. C, cones; H, horizontal cells; B, ON-type cone bipolar cells; t-DA, transient dopamine cells; s-DA, sustained dopamine cells; G, ganglion cells; ipG, melanopsin-expressing intrinsically photoreceptive ganglion cells; PRL, photoreceptor layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer; LGN, lateral geniculate nuclei, the thalamic visual nuclei of the brain that are innervated by conventional ganglion cells; SCN, suprachiasmatic nuclei, the hypothalamic master biological clock nuclei that are innervated by intrinsically photoreceptive ganglion cells.