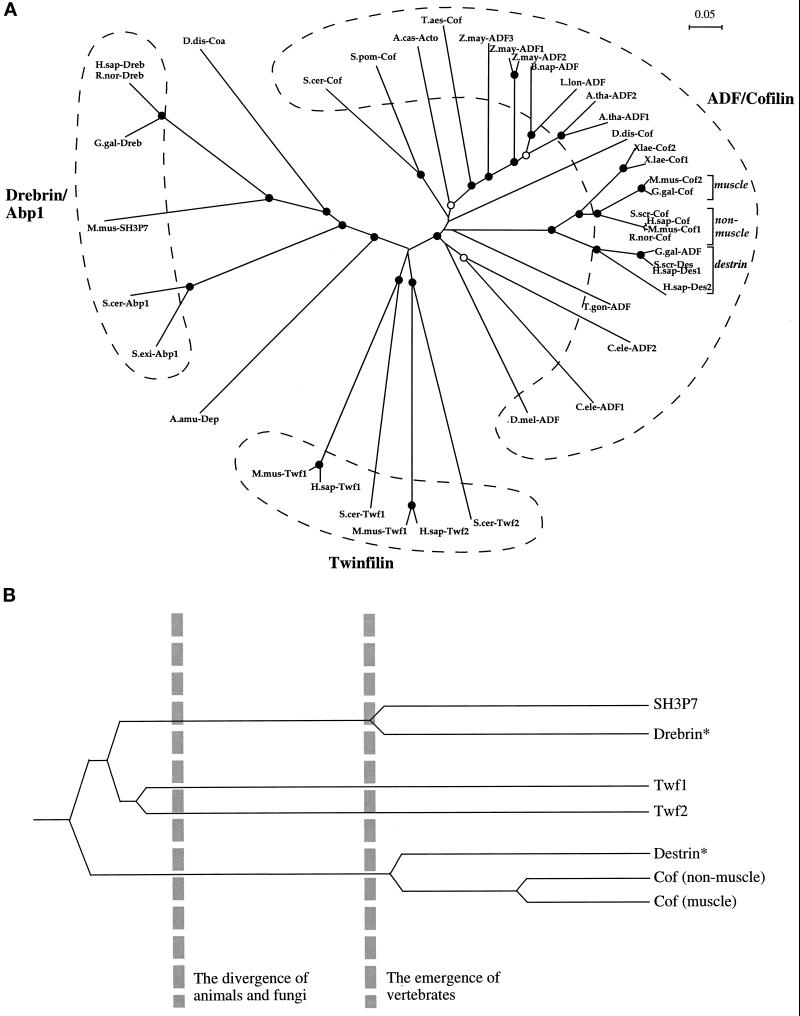
Figure 3.
(A) An unrooted phylogenetic tree of ADF-H domains. This tree was produced by subjecting the alignment depicted in Figure 2 to analysis by the Clustal-W software package (Thompson et al., 1994). An allowance was made for multiple substitutions (Kimura, 1983). Information from intervals in the alignment for which gaps are found in some sequences was included. (Note: the tree architecture is almost identical if gaps are omitted.) The tree was tested (1000 trials) for branching order confidence by bootstrapping (Felsenstein, 1985). Filled circles indicate branch points supported beyond a confidence level of 85%. Empty circles indicate branch points supported beyond the 50% but below the 85% confidence level. Dashed lines indicate the three classes described in this essay. A bar showing 5% divergence is included. Further information on this procedure (as applied to myosin motor domains) can be found on the Worldwide Web at http://www.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/. (B) A simplified, rooted tree depicting the evolution of ADF-H domain proteins in mice. All three families of ADF-H domain proteins were present in the common ancestor of yeast and animals. Distinct members of the ADF/cofilin family in mouse arose after the emergence of vertebrates. The asterisks denote our predictions that destrin- and drebrin-like proteins will be found in mouse, based on the phylogenetic tree shown in A. Protein names, database, and accession numbers for the sequences, respectively, are listed below. Where no database is stated, the accession number refers to GenBank. S. cerevisiae cofilin: Swiss-Prot, Q03048; S. pombe cofilin: DDBJ, D89939; D. discoideum cofilin: Swiss-Prot, P54706; A. castellanii actophorin: Swiss-Prot, P37167; A. thaliana ADF1: U48938; A. thaliana ADF2: U48939; L. longifolium ADF: PIR, S30935; Brassica napus ADF: PIR, S30934; Z. mays ADF1: Swiss-Prot, P46251; Z. mays ADF2: X97725; Z. mays ADF3: X97726; Triticum aestivum cofilin: U58278; Drosophila melanogaster ADF: PIR, A57569; Caenorhabditis elegans ADF1: Swiss-Prot, Q07750; C. elegans ADF2 (Swiss-Prot: Q07749), T. gondii ADF: U62146; H. sapiens destrin 2:(U47924; H. sapiens destrin 1: PIR, A54184; S. scrofa destrin: DDBJ, D90053; Gallus gallus ADF: J02912; R. norvegicus cofilin: Swiss-Prot, P45592; Mus musculus cofilin (nonmuscle isoform): Swiss-Prot, P18760; H. sapiens cofilin: EMBL, X95404; S. scrofa cofilin: M20866; G. gallus cofilin: M55659; M. musculus cofilin (muscle isoform): Swiss-Prot, P45591; X. laevis cofilin 1: U26270; X. laevis cofilin 2: Swiss-Prot, P45593; M. musculus twinfilin (repeat-1): U82324; H. sapiens twinfilin (repeat-1): PIR, A55922; S. cerevisiae twinfilin (repeat-1): SGD, YGR080W; M. musculus twinfilin (repeat-2): U82324; H. sapiens twinfilin (repeat-2): PIR, 55922; S. cerevisiae twinfilin (repeat-2): SGD, YGR080W; H. sapiens drebrin E: Swiss-Prot, Q16643; R. norvegicus drebrin A: Swiss-Prot, Q07266; G. gallus drebrin A, E1 and E2: Swiss-Prot, P18302; M. musculus SH3P7: GenBank, U58884; D. discoideum coactosin: Swiss-Prot, P34121; S. cerevisiae Abp1: EMBL, X51780/Swiss-Prot, P15891; S. exiguus Abp1: Swiss-Prot, P38479; A. amurensis depactin: Swiss-Prot, P20690.