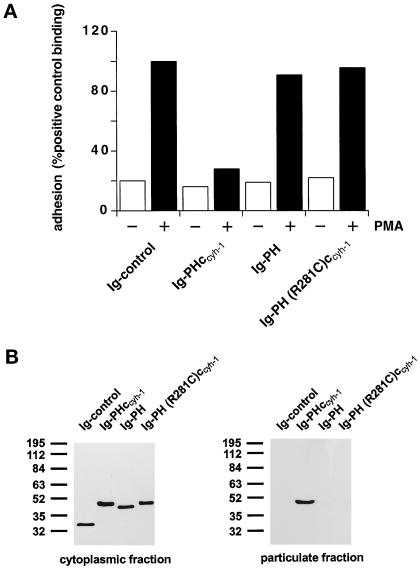
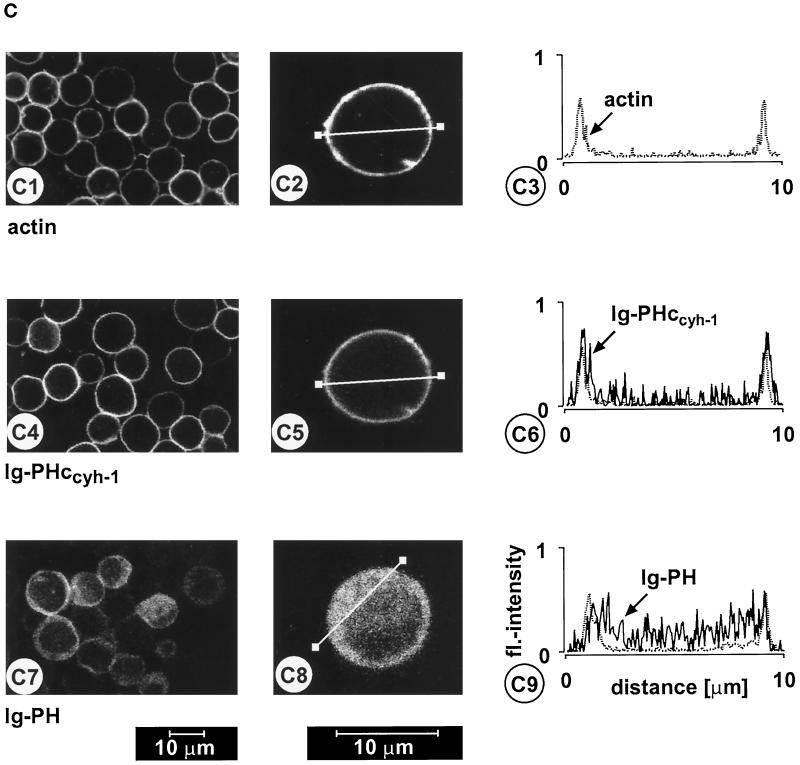
Figure 3.
(A) Adhesion assay. The intact PH domain and the adjacent c domain of cytohesin-1 are both required for dominant inhibition of Jurkat cell adhesion to ICAM-1. Cytoplasmic Ig fusion constructs were expressed using recombinant vaccinia viruses, and the adhesion assay was performed as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. Normalization was performed against the positive control (Ig-control + PMA). (B) Cellular fractionation assay. The intact PH domain and the adjacent c domain of cytohesin-1 are both required for particulate association in Jurkat cells. “Particulate fraction” denotes a crude lysate of cellular membranes. The Ig-control, which is exclusively expressed in the cytoplasm, serves as an internal control for cellular fractionation. (C facing page) Confocal laser scans of the subcellular localization of cytohesin-1 subdomain constructs Ig-PH (C7–C9) and Ig-PHccyh-1 (C4–C6), respectively. Ig fusion proteins were visualized with an FITC-conjugated anti-human IgG Fcγ-specific antibody. For quantitation of subcellular localization, cells were double stained with FITC-labeled anti-Ig (Fcγ) for the respective fusion protein and with TRITC-labeled phalloidin for the visualization of actin. Actin only is shown in C1–C3. Staining intensities measured according to pixel brightness were quantified along cell transects for each construct in a representative positively stained cell. The large, central unstained region visible in C8 is due to the nucleus.