Figure 6.
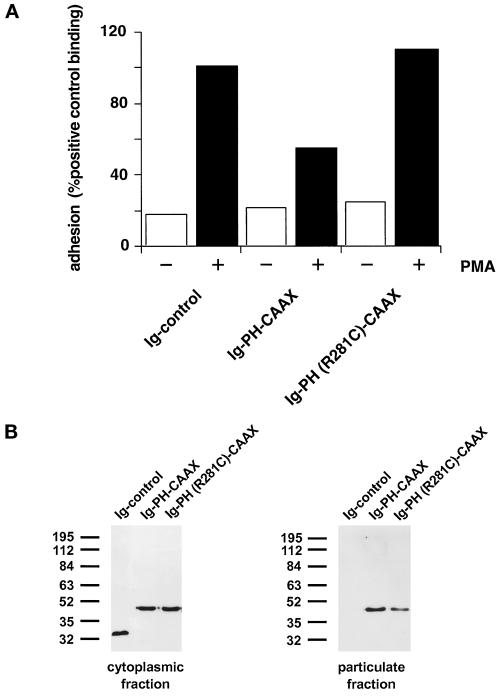
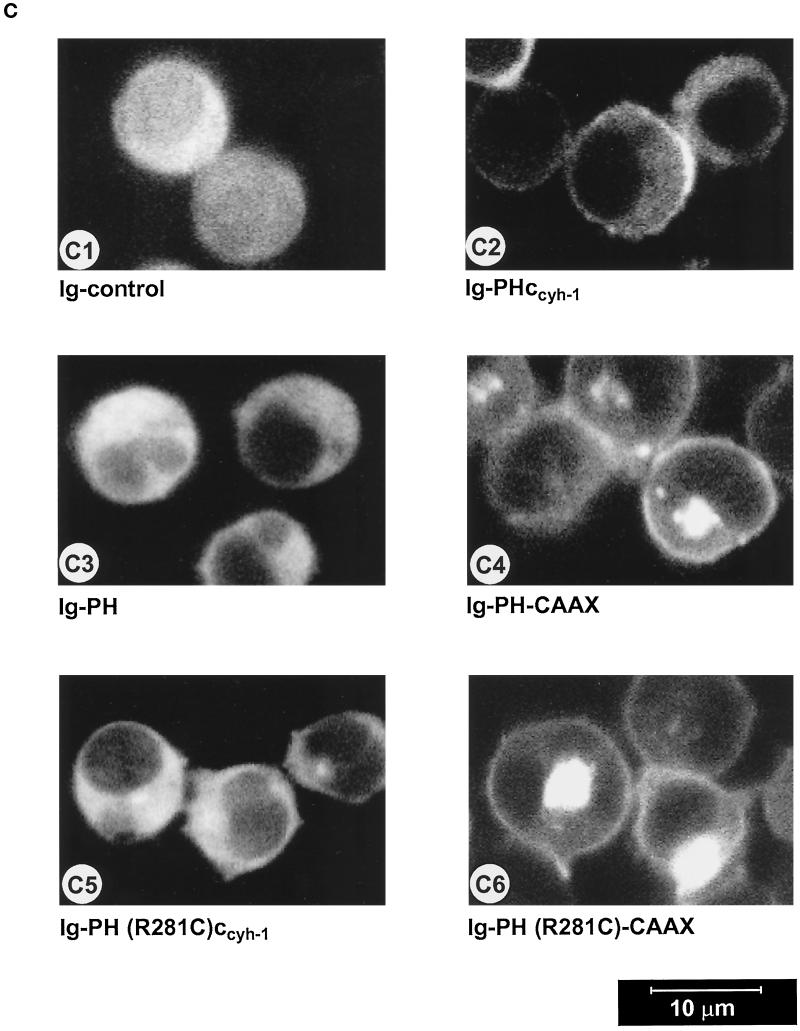
(A) Adhesion assay of cytohesin-1 PH-CAAX chimeras. Replacement of the c domain with a CAAX motif partially restores the dominant inhibition of Jurkat cell adhesion by the PH domain of cytohesin-1. (B) Cellular fractionation of cytohesin-1 PH-CAAX chimeras. The CAAX motif is sufficient for particulate association of cytoplasmic Ig fusion proteins in Jurkat cells. (C facing page) Confocal laser scans of the subcellular distribution of various intracellular Ig fusion proteins derived from cytohesin-1. C1 (Ig control), C3, (Ig-PH), and C5 [Ig-PH (R281C)ccyh-1] show diffuse cytoplasmic localization of the Ig chimeras. In addition to some cytoplasmic staining, C2 (Ig-PHccyh1) exhibits pronounced plasma membrane staining of the respective chimera due to intact PH and c domains. PH domain chimeras containing the CAAX motif Ig-PH-CAAX (C4) and Ig-PH (R281C)-CAAX (C6) appear both in the plasma membrane and within a perinuclear compartment. Ig fusion proteins were visualized with an FITC-conjugated anti-human IgG Fcγ-specific antibody.