Abstract
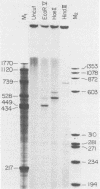
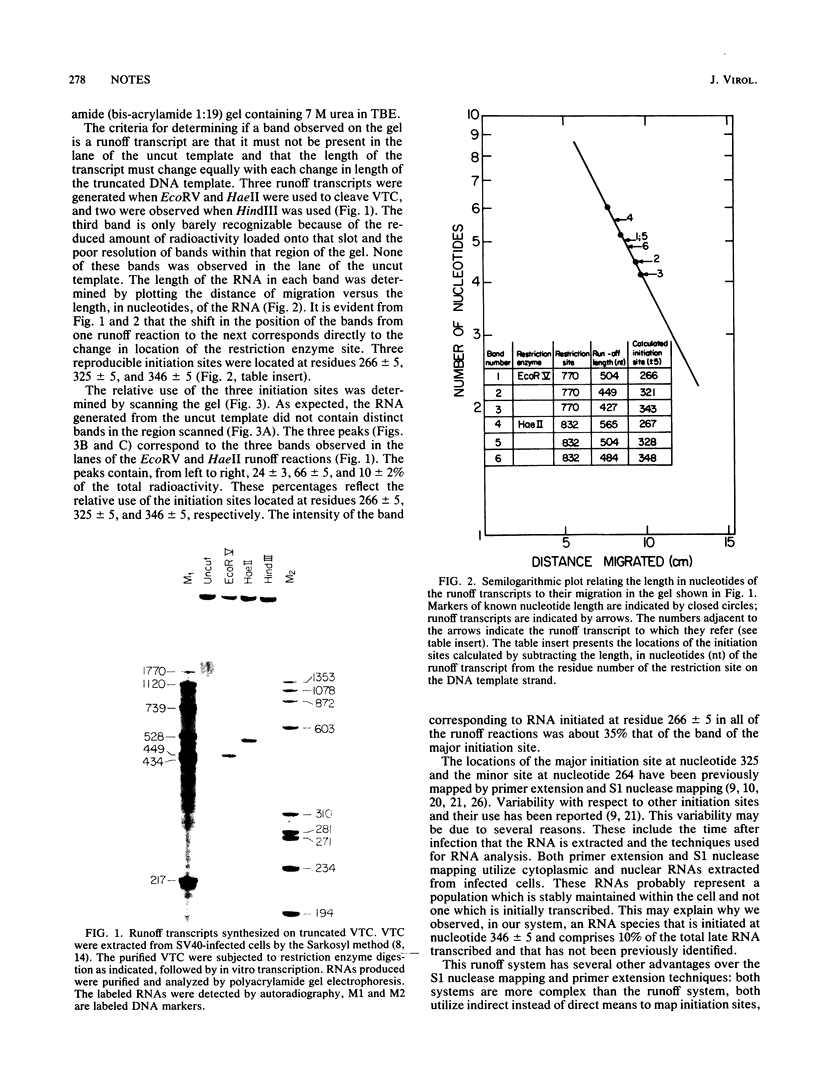
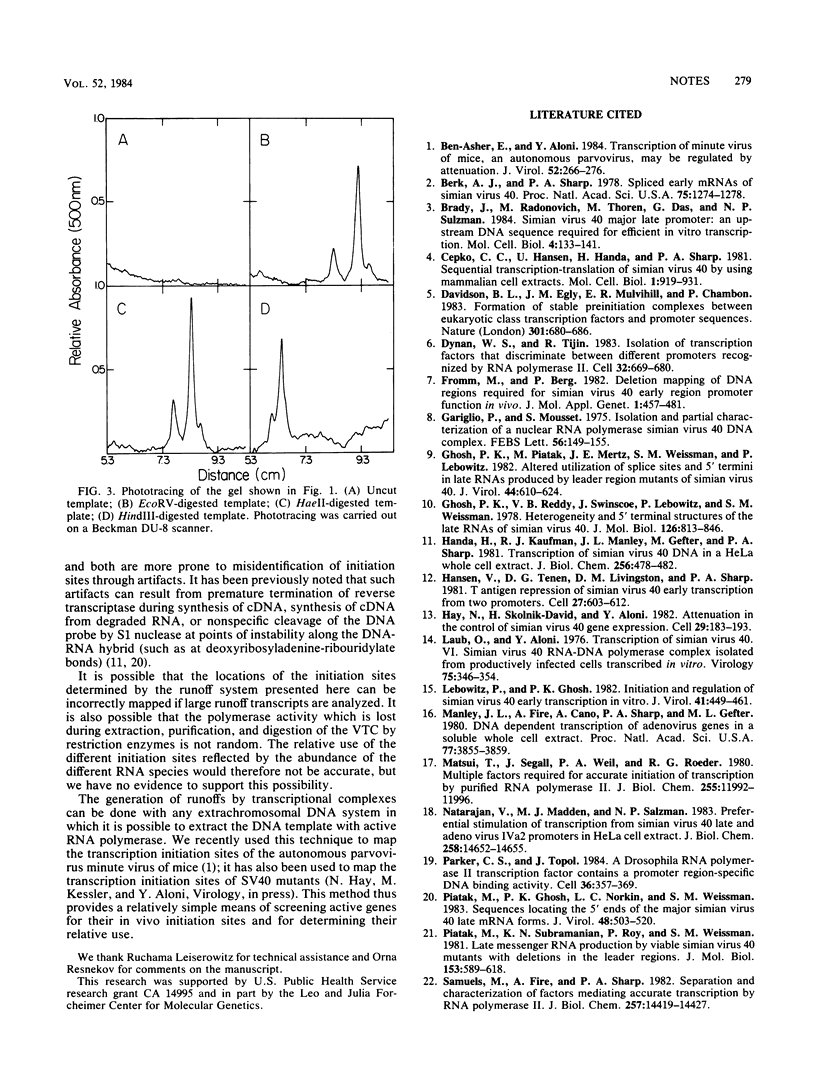
Runoff transcripts were generated on viral transcriptional complexes cleaved with restriction enzymes and incubated in vitro with [alpha-32P]UTP under pulse-chase conditions. As viral transcriptional complexes in vitro elongated the nascent RNA preinitiated in vivo, size analysis by gel electrophoresis of the runoff transcripts allowed identification of the in vivo initiation sites. Moreover, scanning the intensities of the runoff bands as they appeared in the autoradiogram of the gel allowed determination of the relative use of these sites. A model system in which the initiation sites of simian virus 40 late RNA were identified and their relative use determined is presented.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Asher E., Aloni Y. Transcription of minute virus of mice, an autonomous parvovirus, may be regulated by attenuation. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):266–276. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.266-276.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Radonovich M., Thoren M., Das G., Salzman N. P. Simian virus 40 major late promoter: an upstream DNA sequence required for efficient in vitro transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):133–141. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepko C. L., Hansen U., Handa H., Sharp P. A. Sequential transcription-translation of simian virus 40 by using mammalian cell extracts. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;1(10):919–931. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.10.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Isolation of transcription factors that discriminate between different promoters recognized by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Berg P. Deletion mapping of DNA regions required for SV40 early region promoter function in vivo. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):457–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gariglio P., Mousset S. Isolation and partial characterization of a nuclear RNA polymerase - SV40 DNA complex. FEBS Lett. 1975 Aug 1;56(1):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80130-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Piatak M., Mertz J. E., Weissman S. M., Lebowitz P. Altered utilization of splice sites and 5' termini in late RNAs produced by leader region mutants of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):610–624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.610-624.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Swinscoe J., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. Heterogeneity and 5'-terminal structures of the late RNAs of simian virus 40. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):813–846. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa H., Kaufman R. J., Manley J., Gefter M., Sharp P. A. Transcription of Simian virus 40 DNA in a HeLa whole cell extract. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):478–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen U., Tenen D. G., Livingston D. M., Sharp P. A. T antigen repression of SV40 early transcription from two promoters. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):603–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90402-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay N., Skolnik-David H., Aloni Y. Attenuation in the control of SV40 gene expression. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):183–193. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laub O., Aloni Y. Transcription of simian virus 40. VI. SV 40 DNA-RNA polymerase complex isolated from productively infected cells transcribed in vitro. Virology. 1976 Dec;75(2):346–354. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebowitz P., Ghosh P. K. Initiation and regulation of simian virus 40 early transcription in vitro. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):449–461. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.449-461.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Segall J., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors required for accurate initiation of transcription by purified RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11992–11996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan V., Madden M. J., Salzman N. P. Preferential stimulation of transcription from simian virus 40 late and adeno IVa2 promoters in a HeLa cell extract. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14652–14655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piatak M., Ghosh P. K., Norkin L. C., Weissman S. M. Sequences locating the 5' ends of the major simian virus 40 late mRNA forms. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):503–520. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.503-520.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piatak M., Subramanian K. N., Roy P., Weissman S. M. Late messenger RNA production by viable simian virus 40 mutants with deletions in the leader region. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 15;153(3):589–618. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90409-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels M., Fire A., Sharp P. A. Separation and characterization of factors mediating accurate transcription by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14419–14427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shani M., Birkenmeier E., May E., Salzman N. P. Properties of simian virus 40 transcriptional intermediates isolated from nuclei of permissive cells. J Virol. 1977 Jul;23(1):20–28. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.1.20-28.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik-David H., Aloni Y. Pausing of RNA polymerase molecules during in vivo transcription of the SV40 leader region. EMBO J. 1983;2(2):179–184. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01402.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Chambon P. Transcription from the SV40 early-early and late-early overlapping promoters in the absence of DNA replication. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1605–1611. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Luse D. S., Segall J., Roeder R. G. Selective and accurate initiation of transcription at the Ad2 major late promotor in a soluble system dependent on purified RNA polymerase II and DNA. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):469–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]