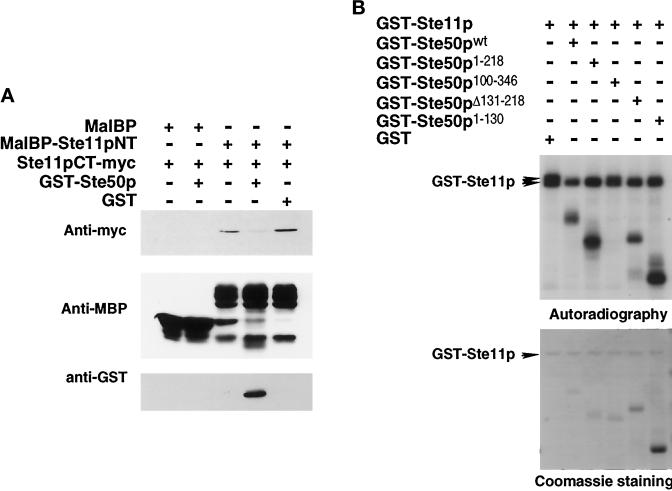
Figure 6.
Ste50p blocks the N-terminal regulatory domain of Ste11p from binding to its C-terminal catalytic domain and is itself an in vitro substrate for Ste11p kinase. (A) Ste50p prevents the N-terminal regulatory domain of Ste11p from binding to the C-terminal catalytic domain of Ste11p. The myc-tagged C-terminal domain of Ste11p (Ste11CT-myc) and Ste50p were expressed as GST fusion proteins and purified from E. coli. The N-terminal domain of Ste11p was expressed in E. coli as an MalBP fusion protein, purified, and immobilized on amylose agarose beads. The beads were then incubated with ∼1 μg of purified myc-tagged C-terminal domain of Ste11p for 30 min at 4°C in the presence of ∼1 μg of either GST-Ste50p or GST alone. The beads were then washed, resuspended into sample loading buffer, and subjected to SDS-PAGE. Immunoblot analyses were then performed with anti-myc (9E10) monoclonal antibody or anti-GST polyclonal antibodies or anti-MalBP polyclonal antibodies using the ECL detection system. (B) Ste50p influences Ste11p kinase activity and is itself a substrate for Ste11p kinase in vitro. GST-Ste11p, various GST-Ste50p constructs, and GST were expressed and purified from yeast strain YCW555 (ssk2Δ ssk22Δ ste11Δ ste50Δ). In vitro kinase assays were performed with ∼250 ng of GST-Ste11p with 250 ng GST or GST-Ste11p in the presence of various GST-Ste50p. Kinase reactions were stopped and subjected to SDS-PAGE, followed by autoradiography (top panel) and Coomassie staining (bottom panel). GST is not shown.