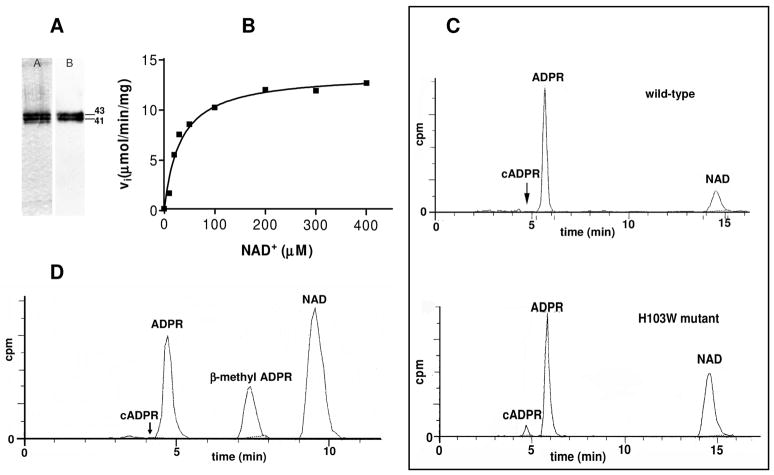
FIGURE 3.
Recombinant soluble H103W SmNACE catalyzed transformation of NAD+. (A) Analysis by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting of purified recombinant H103W SmNACE mutant. Left lane: silver-stained SDS-PAGE gel (12%) – Right lane: immunoblot using anti-NACE antibody (16). The molecular weights (kDa) of the purified mutant are indicated. (B) Kinetics of NAD+ transformation catalyzed by H103W SmNACE mutant. Assays were carried out at 37°C in 10 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.4. Initial rates were determined at the given substrate concentrations and the data were fitted to the Michaelis-Menten equation. (C) Representative HPLC radiochromatograms of the reaction products observed after transformation of 14C-labeled NAD+ by WT (upper panel) and H103W mutant SmNACE (lower panel). The assays were performed at 37°C in 10 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, in the presence of [14C]NAD+ and the reaction products were monitored by radiodetection. (D) Representative HPLC elution profile of the products obtained by solvolysis of NAD+ catalyzed by the H103W SmNACE mutant in the presence of 3.0 M methanol. The methanolysis peak was identified by co-elution with an authentic sample of β-methyl ADPR (57).