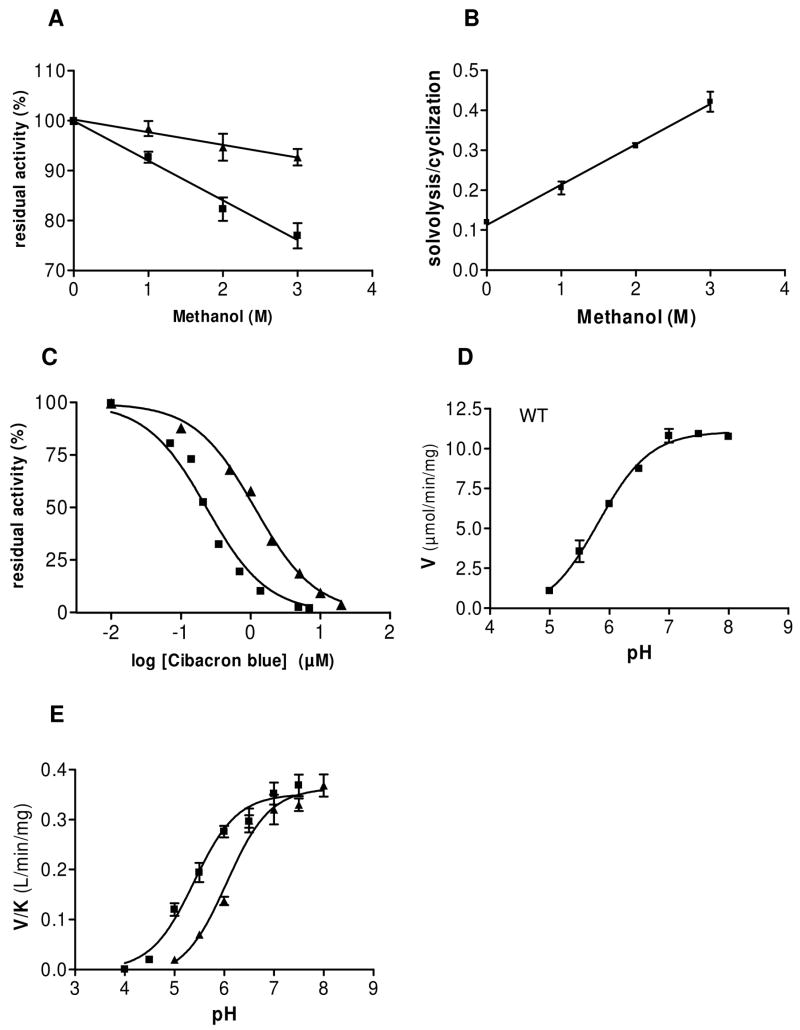
FIGURE 4.
Effect of methanol, Cibacron blue F3GA and pH on reactions catalyzed by SmNACE. (A) Effect of increasing concentrations of methanol on the rate of transformation of 100 μM NGD+ into cGDPR catalyzed by WT (squares) and H103W mutant (triangles) of SmNACE. The assays were carried out at 37°C in 10 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, and the cyclization reaction progress monitored fluorometrically at λem = 410 nm (λexc = 310nm). Residual activities (means ± SD, n=4) are percent of the activity measured in the absence of solvent. (B) Effect of methanol on the solvolysis/cyclization ratio ( = [GDPR + β-methyl GDPR]/[cGDPR]) observed on transformation of 100 μM NGD+ catalyzed by WT SmNACE (means ± SD, n=3). The reaction products were analyzed by HPLC and their relative proportions were quantified as described previously (8). (C) Inhibition of WT and H103W SmNACE by Cibacron blue F3GA. The effect of the Cibacron blue on the initial rates of the transformation of 20 μM 1,N6-etheno-NAD+ catalyzed by SmNACE in 10 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, was followed fluorometrically (λem = 410 nm; λexc = 310 nm) at 37°C. The IC50 values were calculated from the plot of residual activity against log of dye concentration. WT (triangles) and H103W SmNACE mutant (squares). (D) pH dependence of WT SmNACE. The pH profile of Vmax, measured at 37°C, using 1,N6-etheno-NAD+ as substrate displayed a critical ionization with a pKa of 5.82 ± 0.07 which must be unprotonated for catalytic activity. (E) pH profiles of Vmax/Km values determined at 37°C using 1,N6-etheno-NAD+ as substrate (n = 3). WT (triangles) and H103W SmNACE mutant (squares). In (D) and (E) the solid lines represent the fit of the data (n = 3) to a single pKa model.