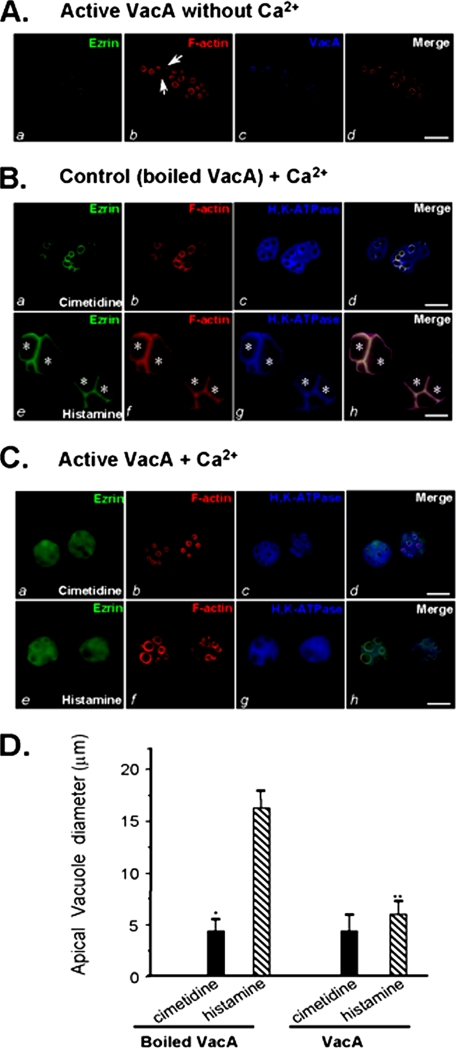
FIGURE 4.
VacA-induced hydrolysis of ezrin results in an inhibition of acid secretion in cultured parietal cells. A, cultured parietal cells were incubated with VacA (5 μg/ml) on ice for 3 min, followed by washout of unbound VacA and warming at 37 °C for 20 min in the absence of extracellular calcium. The treated cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained for ezrin, F-actin, and VacA. Ezrin marks the apical membrane of parietal cells (a), which is overlapped with the labeling of VacA (d). Bar, 10 μm. B, cultured parietal cells were incubated with inactive (boiled) VacA (5 μg/ml) in the presence of 1.8 mm Ca2+ for 5 min followed by a 20-min incubation with histamine or cimetidine. Treated cells were fixed and stained for ezrin, F-actin, and H,K-ATPase. Bar, 10 μm. C, cultured parietal cells were incubated with active VacA (5 μg/ml) for 5 min in the presence of 1.8 mm Ca2+ prior to a 20-min incubation with histamine or cimetidine. Treated cells were fixed and stained for ezrin, F-actin, and H,K-ATPase. Bar, 10 μm. D, cultured parietal cells were incubated with active VacA or inactive VacA for 20 min prior to stimulation with histamine plus IBMX. The diameters of apical vacuoles were measured as an index for apical membrane expansion associated with acid secretion. Data were obtained from resting and stimulated parietal cells in which apical vacuoles were in the same focal plane. These measurements were taken from four different preparations in which 75 cells from each category were examined. In resting cells, measurements were carried out on 2-5 vacuoles/cell, whereas 1-3 vacuoles/cell were analyzed in stimulated preparations. Data are expressed as means ± S.E.