FIGURE 6.
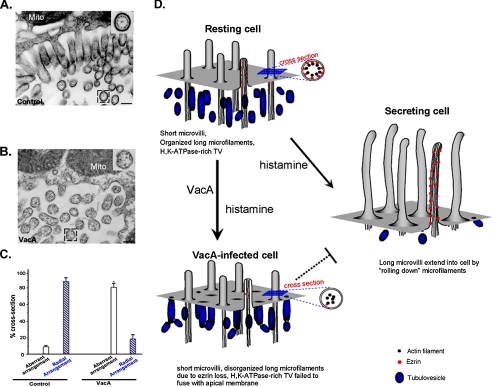
VacA-induced hydrolysis of ezrin disrupts the actin cytoskeleton-membrane association. A, microfilaments are highly organized in the apical microvilli of gastric parietal cells. Secreting gastric glands were processed as described under “Materials and Methods.” Thin sections were poststained with uranyl acetate and lead citrate and examined under an electron microscopy. In control secreting parietal cells, the greatly expanded apical membrane is lined with numerous elongated microvilli. A magnified view of a cross-section (inset) shows the radial arrangement of the actin filaments in proximity to the microvillar membrane in parietal cells. B, microfilaments-membrane association in parietal cell is disrupted by VacA treatment. VacA-treated secreting gastric glands were processed as described in A. In VacA-treated parietal cells, the apical membrane was lined with numerous short microvilli. A magnified view of a cross-section (inset) shows an aberrant arrangement of the actin filaments in the microvilli. Bar, 200 nm. C, statistics of actin filament arrangements seen in the cross-sections of parietal cell microvilli from both VacA-treated and control parietal cells. Values represent the means ± S.E. of at least 120 microvillar cross-sections in 11 different cells. D, hypothetical scheme accounting for VacA-induced hypochlorhydria. In the resting cell, short, apical microvilli are supported by long microfilaments extending deep into the cytoplasm. Ezrin (red dot) links actin filaments with the apical plasma membrane. Stimulation leads to docking and fusion of H,K-ATPase-rich tubulovesicles to the apical plasma membrane, greatly expanding the apical surface. Interactions between the apical membrane and microfilaments, via ezrin, reorganize the expanded surface into long microvilli. However, VacA induces proteolysis of ezrin, which disrupts the interactions between the apical membrane and microfilaments, which prevents the recruitment of H,K-ATPase to the apical membrane. Defective recruitment of H,K-ATPase to the apical membrane results in hypochlorhydria in VacA-infected parietal cells.