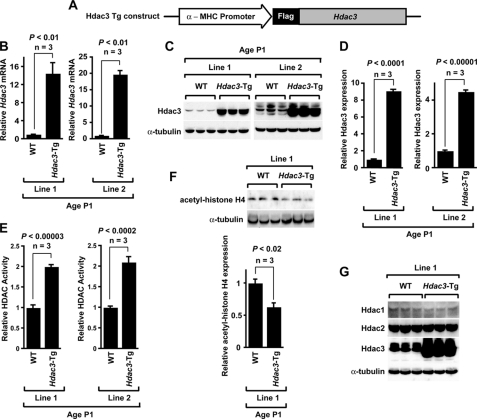
FIGURE 1.
Generation and characterization of cardiac myocyte-specific Hdac3-Tg mice. A, schematic of transgenic construct used to generate Hdac3-Tg mice. α-MHC, α-myosin heavy chain. B, Hdac3 mRNA expression analysis in two different Hdac3-Tg mice lines. Transcripts for Hdac3 were detected by qRT-PCR in P1 hearts from wild-type (WT) and Hdac3-Tg mice. Three mice in each group were tested, and values are expressed as the -fold change in transcript abundance (± S.D.) when compared with wild-type mice. C, endogenous and transgenic Hdac3 protein were detected with an Hdac3 antibody. All Western blots were performed at least three times with similar results. D, Hdac3 expression in myocardium of P1 wild-type and Hdac3-Tg mice was quantified by using ImageJ software. E, increased HDAC activity in Hdac3-Tg mice. Lysates from P1 hearts were assayed for HDAC activity. Data are the average results (± S.D.) from three separate experiments. F, decreased acetylation of histone H4 in Hdac3-Tg mice. Western blot analysis of acetylated-histone H4 in myocardium from P1 wild-type and Hdac3-Tg mice using anti-acetyl-histone H4 antibody was performed. ImageJ software was used to quantify -fold change in acetylation. G, Hdac1 and Hdac2 levels are not changed in Hdac3-Tg mice. Western blot analysis of myocardium lysates from three P1 wild-type and three Hdac3-Tg mice using anti-Hdac1 and anti-Hdac2 antibody was performed. α-Tubulin is used as a loading control.