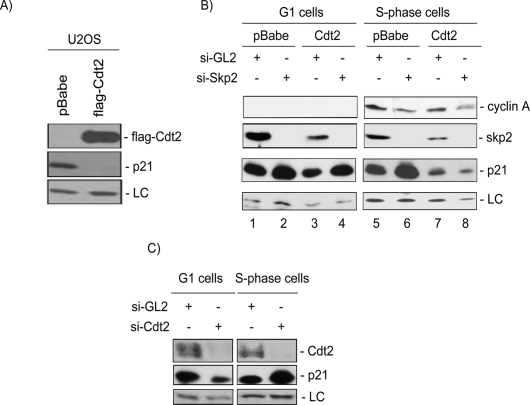
Figure 7.
Cdt2 promotes the destruction of p21 in S-phase cells. (A) Stable expression of Cdt2 significantly reduces the steady-state levels of p21 in asynchronous U2OS cells. Soluble protein lysates of Mock or Cdt2-overexpressing U2OS cells were resolved on SDS-PAGE and analyzed for Cdt2 (anti-Flag) and p21 protein levels. (LC) A cross-reacting band in the anti-p21 blot serving as a loading control. (B) Cdt2 specifically targets p21 in S phase of the cell cycle. Control or Cdt2 overexpressing U2OS cells were transfected either with control siRNA (si-GL2) or with siRNA against Skp2. Forty-eight hours after transfections, cells were synchronized with nocodazole, and mitotic cells were collected by shake-off, washed with PBS, and incubated for an additional 8 h (G1 cells) or 16 h (S-phase cells), and the cell lysates were analyzed for the indicated proteins. Cyclin A levels show the synchronization of cells in G1 (left) and S phase (right) of the cell cycle. The results demonstrate that Skp2 down-regulation by siRNA results in the accumulation of p21 in both G1- and S-phase cells. On the other hand, ectopic expression of Cdt2 significantly reduced p21 only in S-phase cells, and that reduction occurred even after down-regulating Skp2 (lanes 7,8). (C) Endogenous Cdt2 promotes the destruction of p21 during S phase of the cell cycle. HeLa cells transfected with either control si-RNA (si-GL2) or siRNA targeting Cdt2 (si-Cdt2) and synchronized in G1 and S phases of the cell cycle as described in B. Protein lysates were subsequently analyzed as in B. The anti-Cdt2 blot demonstrates efficient down-regulation of Cdt2 in cells transfected with si-Cdt2. (LC) A cross-reactive band in the anti-p21 blot used as loading control. The results demonstrate that p21 protein is specifically stabilized in S-phase cells but not in cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle upon depletion of Cdt2.