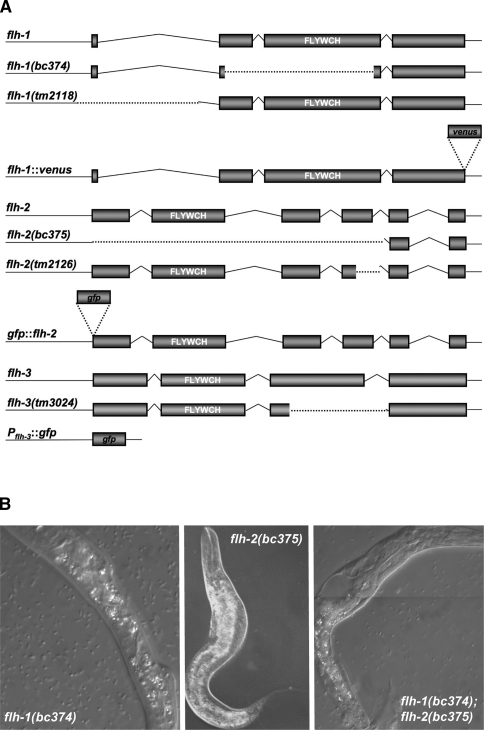
Figure 2.
(A) Schematic of the flh-1, flh-2, and flh-3 loci, mutants, and reporter transgenes. The flh-1 gene encodes two isoforms—FLH-1a and FLH-1b—that differ by three amino acids (Fig. 1C). In this study, we refer to the product of flh-1a as “FLH-1.” The nature of the flh-1(bc374) and flh-2(bc375) mutations is described under Results. The flh-1(tm2118) is a 707-bp deletion, from 287 bp upstream to 419 bp downstream of the translational start codon. The flh-2(tm2126) lesion is a 348-bp deletion. The flh-3 locus is immediately upstream of flh-1 and is transcribed in the opposite orientation. The flh-3(tm3024) mutant allele is a 337-bp deletion of most of exon 3. A description of the fluorescent transgenes can be found in the Materials and Methods. The white letters indicate the location of the FLYWCH domain. Dotted lines delineate deleted regions. The figure is not drawn to scale. (B) Phenotype of FLH-1 and FLH-2 mutants. Animals were observed using Nomarski DIC microscopy. (Left and middle panels) Single mutants of flh-1(bc374) and flh-2(bc375) exhibit a nearly wild-type phenotype with a low penetrance of larvae with morphological abnormalities. (Right panel) The double flh-1(bc374); flh-2(bc375) mutation also results in young larvae with morphological aberrations as well as a complete penetrance of early larval lethality.