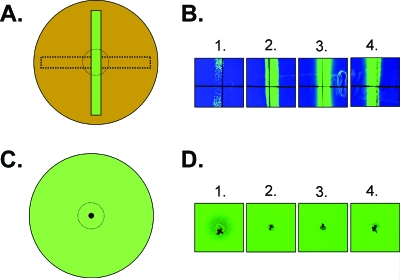
FIG. 2.
MccH47 sensitivity assays for CVD 908-htrA carrying plasmids pGEN222 (lanes 1), pGENMch (lanes 2), pGENMchK2 (lanes 3), and pGEN222I (lanes 4). (A and B) The cross-streaking method for resistance to MccH47. An overnight culture of RYC1000(pEX4) was swabbed from left to right across 2× LB50 plates and allowed to grow overnight at 37°C to impregnate the medium with MccH47 (A, dotted horizontal rectangle). Excess bacterial growth then was removed from the surface, and remaining bacteria were lysed with chloroform. CVD 908-htrA carrying plasmids expressing GFPuv with or without MchI then were streaked orthogonally to the MccH47 zone (A, vertical green rectangle), and plates were again incubated overnight at 37°C. The presence or absence of zones of clearing near the MccH47 region are represented as dotted circles in the graphic; panel B documents these zones for plasmid-bearing CVD 908-htrA live vectors. (C and D) Patch tests for resistance to MccH47. 2× LB50 plates were seeded with a lawn of CVD 908-htrA carrying plasmids expressing GFPuv with or without MchI (C, green circle). The MccH47-expressing strain RYC1000(pEX4) was spotted in the middle of each plate, and plates were incubated at 37°C overnight. The presence or absence of zones of clearing are represented by dotted circles; panel D documents these zones for plasmid-bearing CVD 908-htrA live vectors.